BX Framework
This document describes BX Framework.
1. What is BX Framework?
BX Framework (BXM) provides a development environment for developing applications used by financial institutions and an architecture for running them. As an architecture for financial applications, it provides an online architecture, batch architecture, center-cut architecture, and deferred architecture.
2. Development Environment
It provides an integrated development environment that includes tools to create various components such as IO, DBIO, Service, Bean, and test tools, so that developers can focus on implementing pure business logic and perform rapid and flexible development.
-
Provides various wizards and auto-generation features
-
Provides an integrated development environment that enables integrated design, development, and testing
-
Enforces standardization through real-time code inspection
-
Ensures standard compliance based on wizards and templates
-
Easy search for reusing built modules
-
Eliminates dependencies between modules through a standard I/O structure
-
Supports easy service testing based on messages
-
Supports regression tests and repetitive tests
-
Provides productive development tools for each component such as Service, Bean, IO, DBIO
-
Provides integrated application quality and various test metrics
-
Provides exception and code quality management and debugging features

3. Architecture
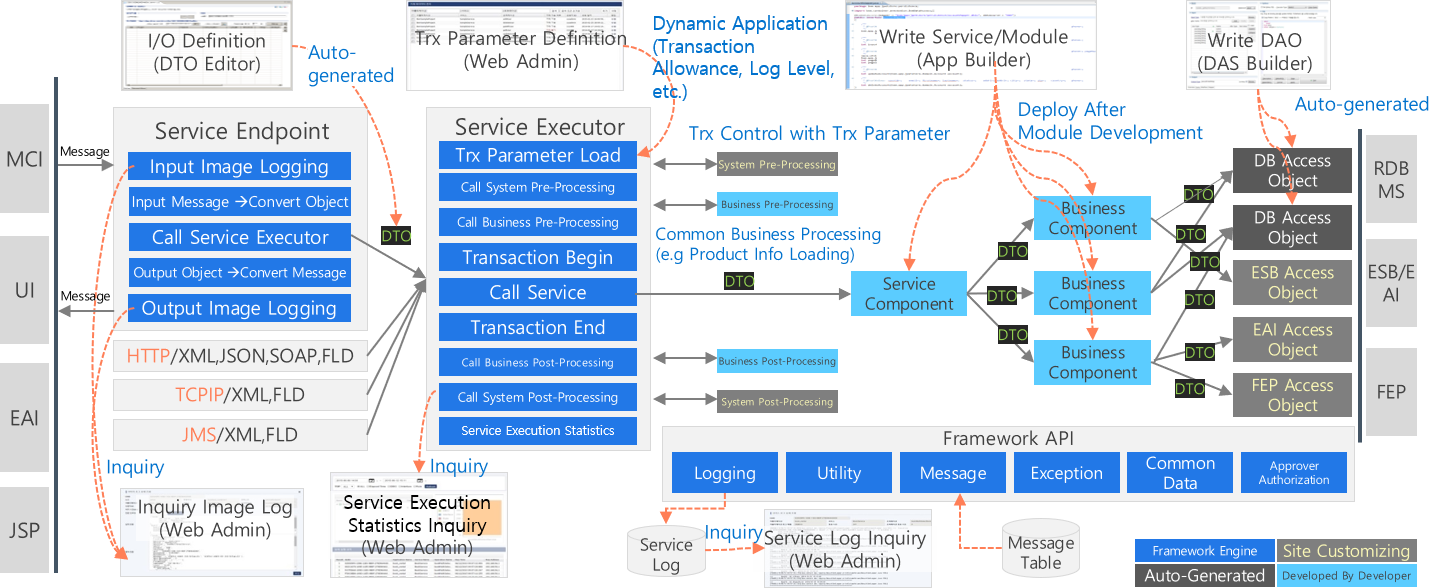
3.1. Online Architecture
The online architecture has a hierarchical processing structure and is separated into channel, service control, business, and interface layers, providing a structure that enables efficient common processing.
-
Channel Layer
-
Supports various protocols and message formats
-
Automatic conversion between messages and DTOs
-
-
Service Control Layer
-
Transaction control and service routing
-
Hierarchical transaction processing structure (pre/post processing)
-
-
Business Layer
-
POJO-based beans
-
Linking between modules through DTOs
-
Singleton-based factory structure
-
-
External Access Layer
-
Standardized DB access
-
Internal/external system interfaces (Sync/Async)
-
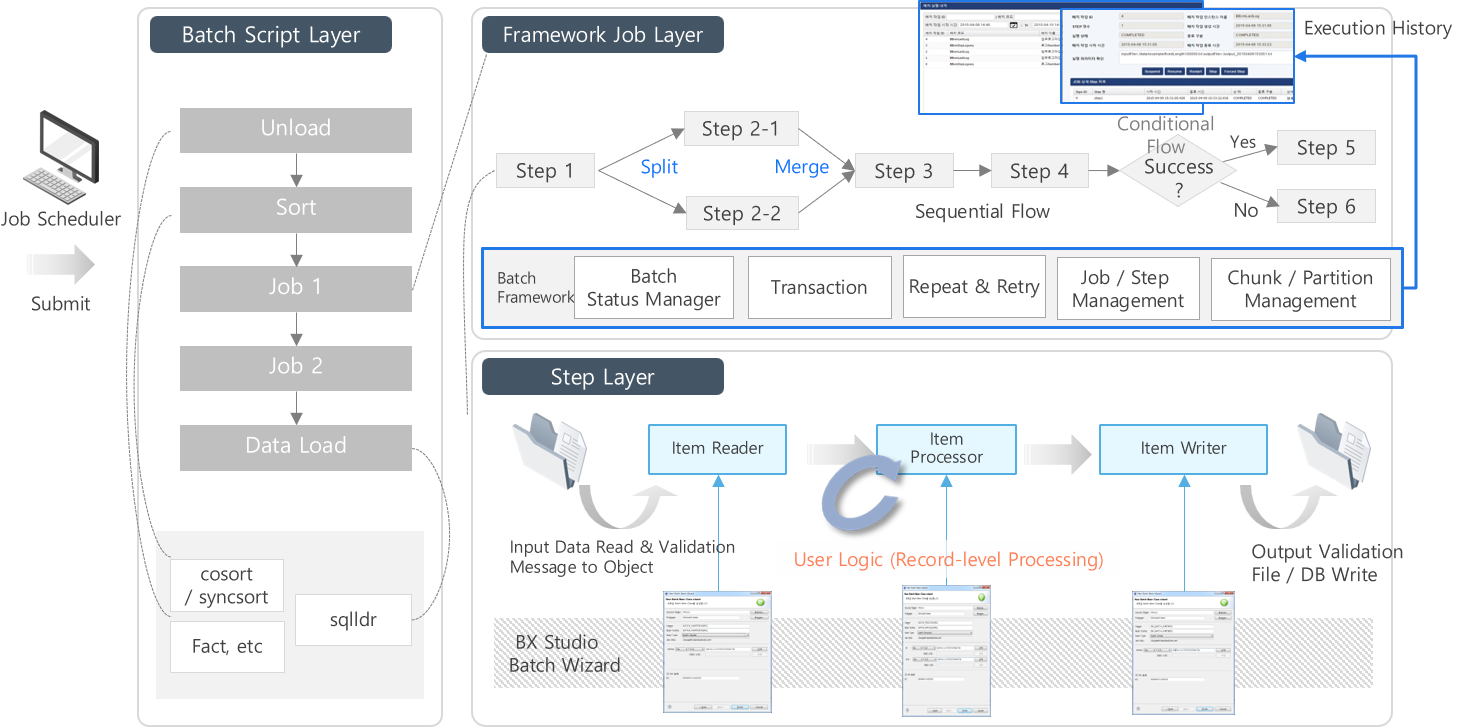
3.2. Batch Architecture
The BX Framework (BXM) batch architecture based on Spring Batch provides a stable execution environment in which large-scale batch jobs can be easily developed and operated. The framework is responsible for the flow of steps and transaction processing, and developers only need to implement the processor that handles a single record.
-
Normal batch
-
Batch that is periodically or non-periodically executed at a specified time by a job scheduler
-
-
Ondemand batch
-
Batch that is invoked and executed from online processing – executed and completed within several minutes (short term)
-
-
Daemon batch
-
Processing batch that is repeatedly executed at fixed intervals
-
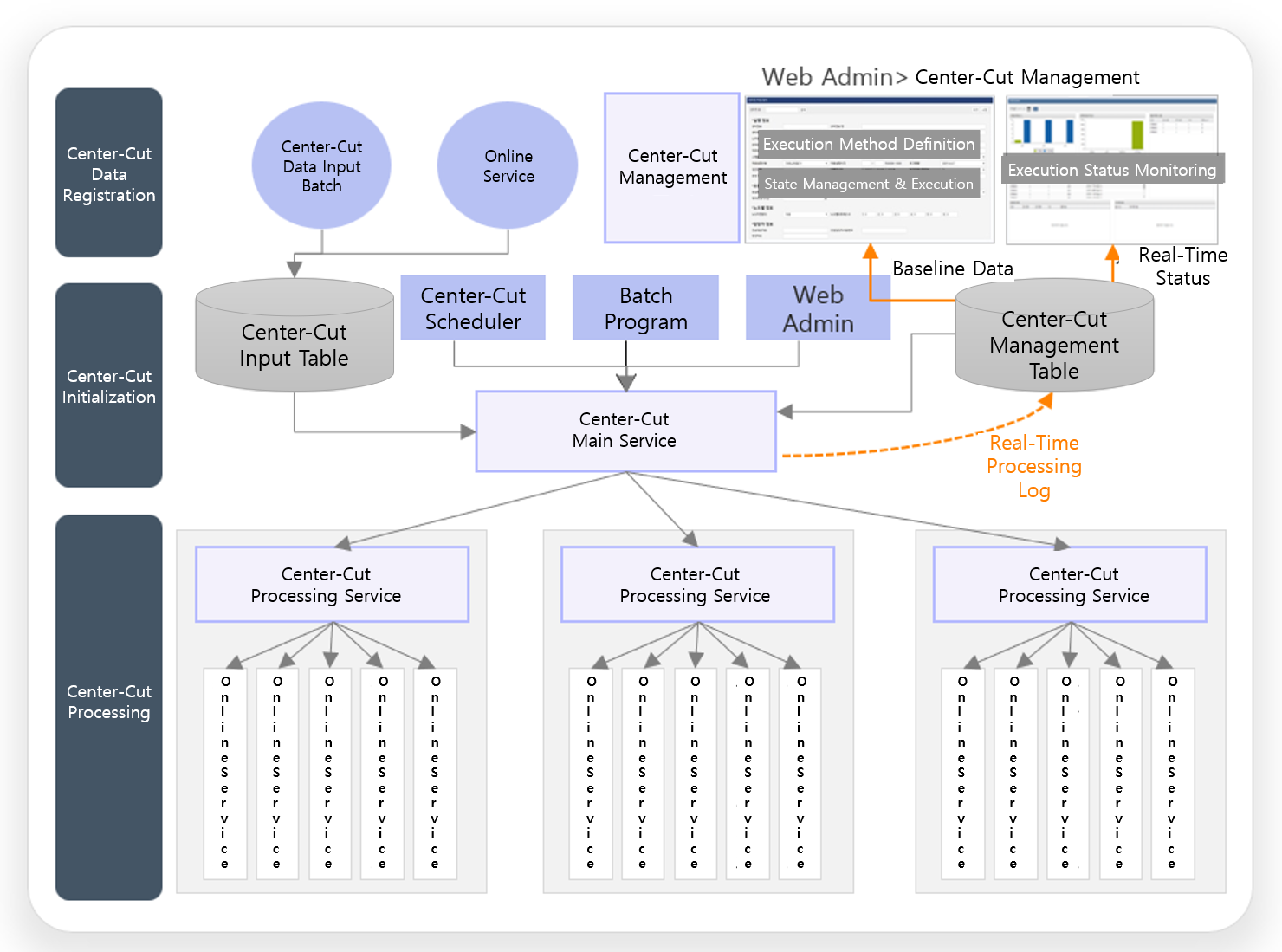
3.3. Center-cut Architecture
It provides job management, Distributed Processing, and Parallel Processing functions, and provides processing patterns that allow developers to freely change the generation of processing targets and recording of results, thereby providing a flexible and high-performance architecture.
-
Classification by job generation and request method
-
Data generation by batch, center-cut start by batch
-
Data generation by batch, center-cut start by scheduler
-
Bulk data generation by online, center-cut start by scheduler
-
Single data generation by online, center-cut start by scheduler
-
-
Classification by Parallel Processing method
-
General parallel
-
Sequential parallel
-
-
Parallel Processing and flow control
-
Supports sequential Parallel Processing
-
Automatically adjusts workload according to processing status per node
-
Real-time dynamic flow control
-
-
Error reprocessing
-
Sets whether to automatically stop/continue processing in case of errors according to business characteristics
-
Re-registers error jobs for processing
-
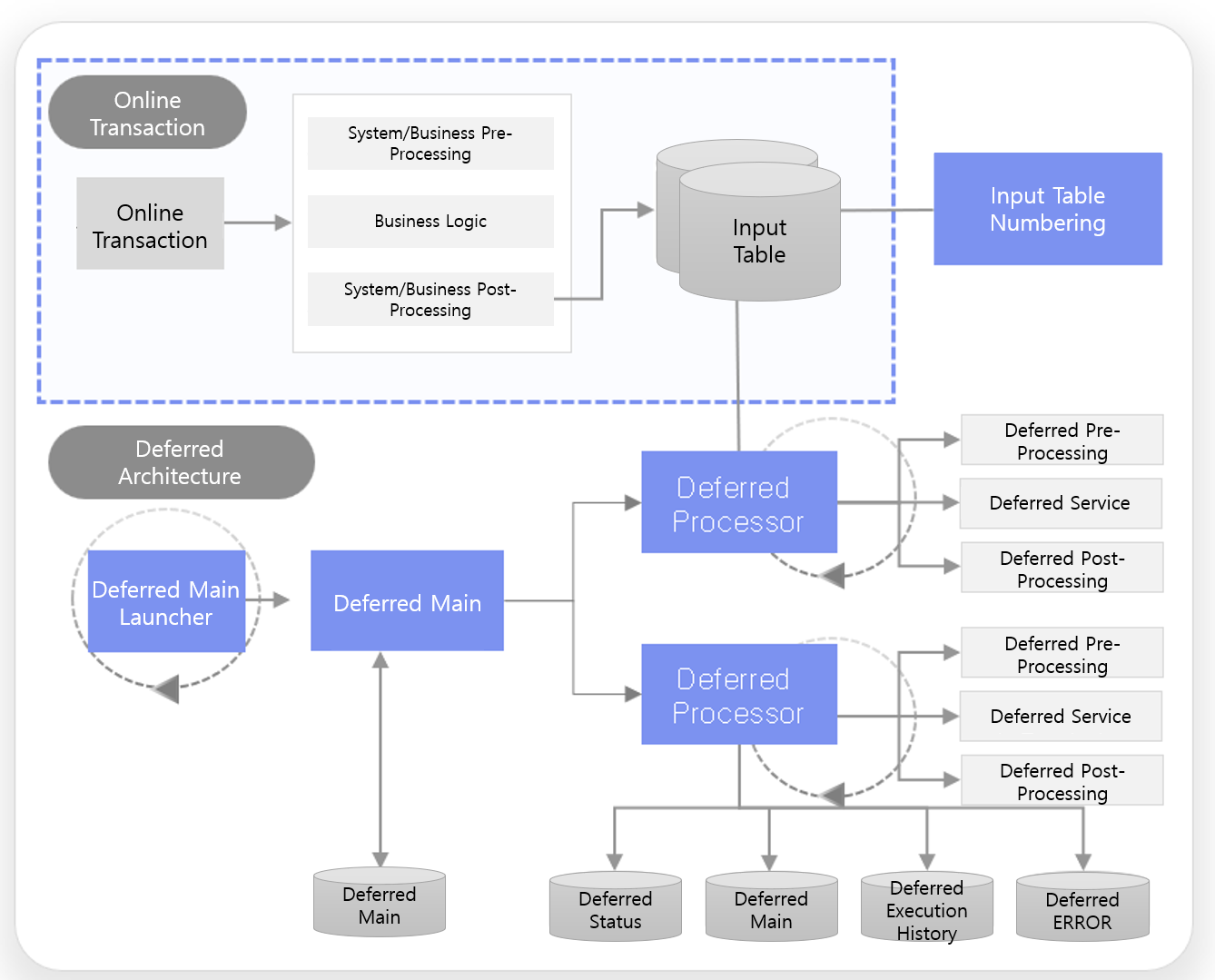
3.4. Deferred Architecture
The deferred process architecture provides various functions to shorten the response time of online transactions by preventing the same ledger lock and to send information that must be transferred to other systems in near real-time from online processing.
-
Business consistency management
-
Deferred management according to business start and end
-
Numbering without gaps for deferred input data
-
Normal/error/unprocessed status for deferred processing data
-
-
High-performance processing
-
High-performance processing in near real time
-
Supports multi-node and Parallel Processing
-
Flow control through real-time dynamic load balancing
-
Guarantees fail-over in the event of failures
-
-
Error reprocessing
-
Sets automatic stop/continue processing in case of errors according to the characteristics of deferred process business
-
Automatic reprocessing and stop condition management for error jobs
-
Trace management for error details
-