Creating Excel Specifications for Batch Projects
The Excel file for the component specifications to be used in batch projects is created in the same way as the Excel file used in online projects.
Batch projects additionally require an Excel file for the Batch Job Specifications.
-
Batch Job Specifications: Defines Job, Step, and Chunk, Tasklet, etc.
Sheets are distinguished not by sheet name but by sheet number (Index).
The sheet number for the Batch Job Specifications sheet is set to 0. To change the sheet order, you can use the
specifications.excel.batchJobSpecifications.batchJobList.sheetIndexoption.
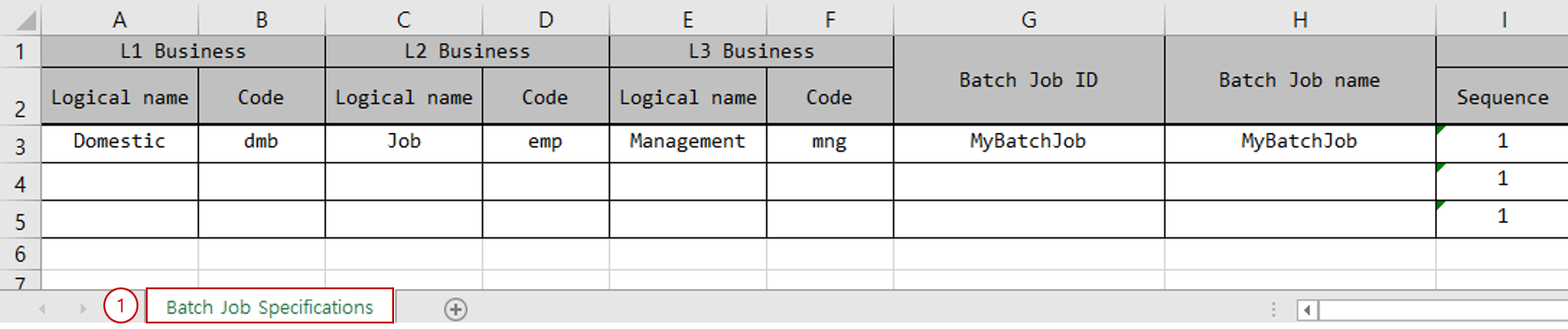
1. Batch Job Specifications Sheet
The batch job specifications sheet must be created as follows.
-
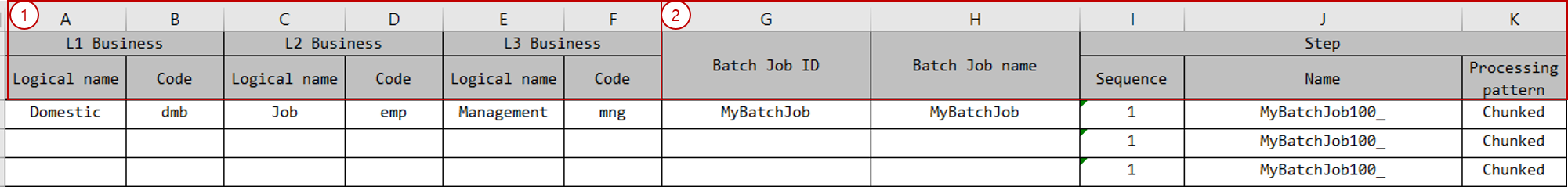
Business Level Code section: Enter the business level codes. Typically, business level codes are combined and used as package names.
Attribute Description Logical name
Enter the logical name of the business level code.
Code
Enter the code for the business level code.
The number of business level codes may vary depending on the development environment. (default 3)
-
Batch Job/Step section: Define batch jobs, steps, and step types.
Attribute Description Batch Job ID
Enter the batch job ID.
Batch Job name
Enter the logical name of the batch job.
Step - Sequence
Enter the processing order of the step.
Step - name
Enter the logical name of the step.
Step - Processing pattern
You can select
TASKLET,CHUNK. -
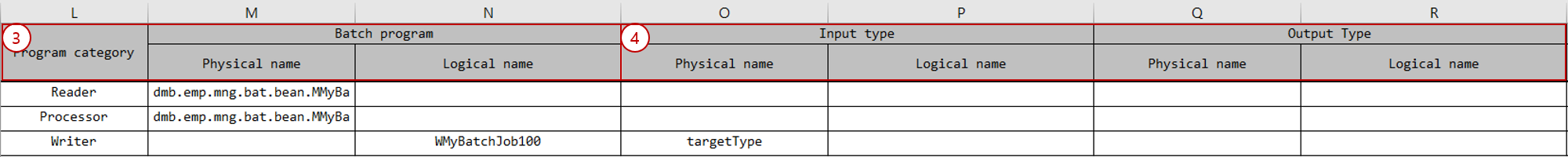
Batch Program section: Define the batch program type and batch program information.
Attribute Description Program category
If the batch processing pattern is TASKLET, you can use
Tasklet; if it is CHUNK, you can useReader,Processor,Writer.Physical name
Enter the physical name of the batch program. If entered as a Full Name, the package name is extracted and used from the Full Name.
Logical name
Enter the logical name of the batch program.
-
I/O Type section: Define the input/output types of the batch program.
Attribute Description Remarks Input - Physical name
Enter the physical name of the input type. You can enter the class name of the IO. If entered as a Simple Name, the business level codes are combined and used as the package name.
Enter only when the batch program type is
Processor,Writer.Input - Logical name
Enter the logical name of the input IO.
Enter only when the batch program type is
Processor,Writer.Output - Physical name
Enter the physical name of the output type. You can enter the class name of the IO. If entered as a Simple Name, the business level codes are combined to derive the package name.
Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Processor.Output - Logical name
Used as the logical name of the output IO.
Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Processor. -
I/O Data section: You can define the types of data to be processed by the batch program.
Attribute Description Remarks Data type
Defines the type of data. You can use
DB,FILE.Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Writer.Data processing type
Defines the data processing type. If the data type is DB, you can use
DBIO; if it is FILE, you can useFIXED,DELIMETED,VARIABLE, etc.Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Writer.Encoding
If the data processing type is FILE, enter the character set to use when processing the data. You can use
UTF8,EUC-KR, etc.Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Writer.Delimiter
If the data processing type is DELEMITED, enter the delimiter for the data. You can use a comma (
,), semicolon (;), etc.Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Writer.IO type
If the batch program type is Reader, you can use
IN; if it is Writer, you can useOUT.Enter only when the batch program type is
Reader,Writer.