Creating Excel Specifications for Online Projects
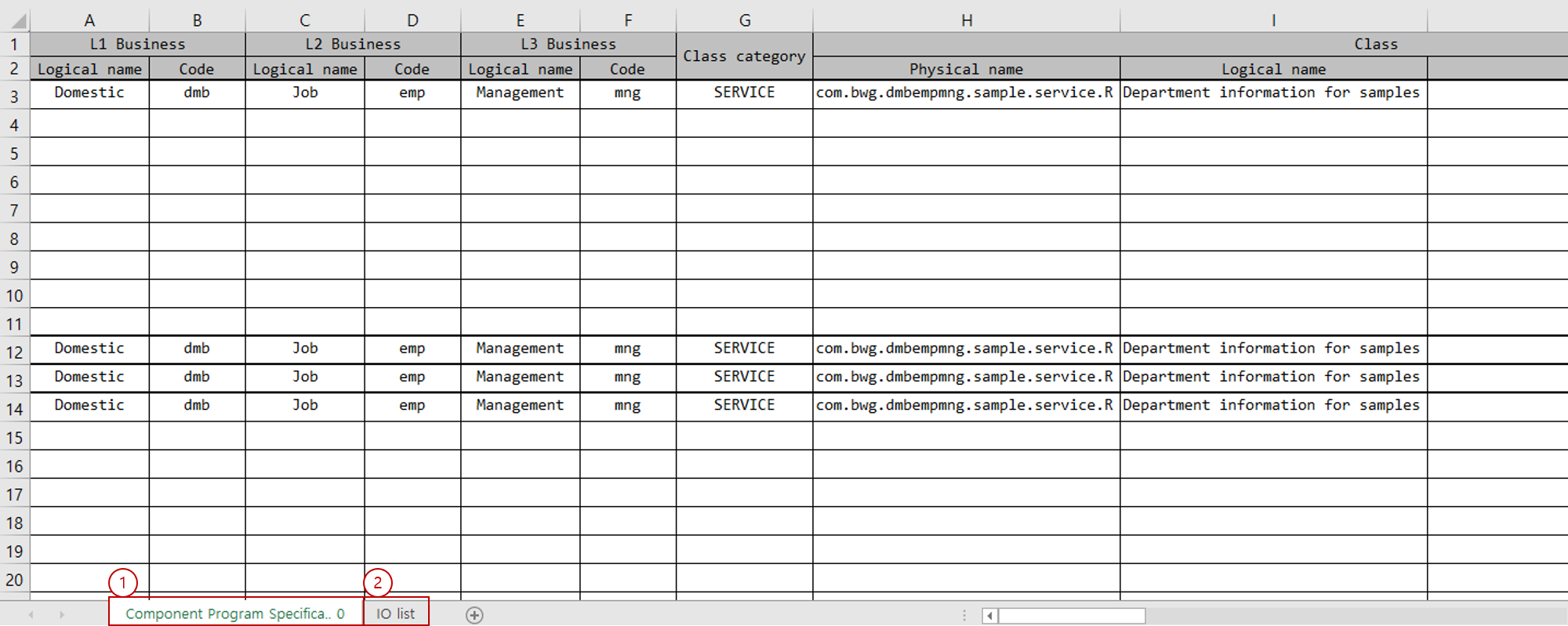
The component specification Excel file consists of the Component Program Specifications and IO List sheets.
The data written in each sheet is read to generate components such as Service, Bean, DBIO, IO, and so on.
-
Component Program Specifications: Write class information for Service, Bean, DBIO components and program processing order.
-
IO List: Write class information and field list for IO.
Each sheet is distinguished by its index number, not by the sheet name.
|
The index number of the Component Program Specifications sheet is set to 0. To change the sheet order, use the The index number of the IO List sheet is set to 1. To change the sheet order, use the |
1. How to write data
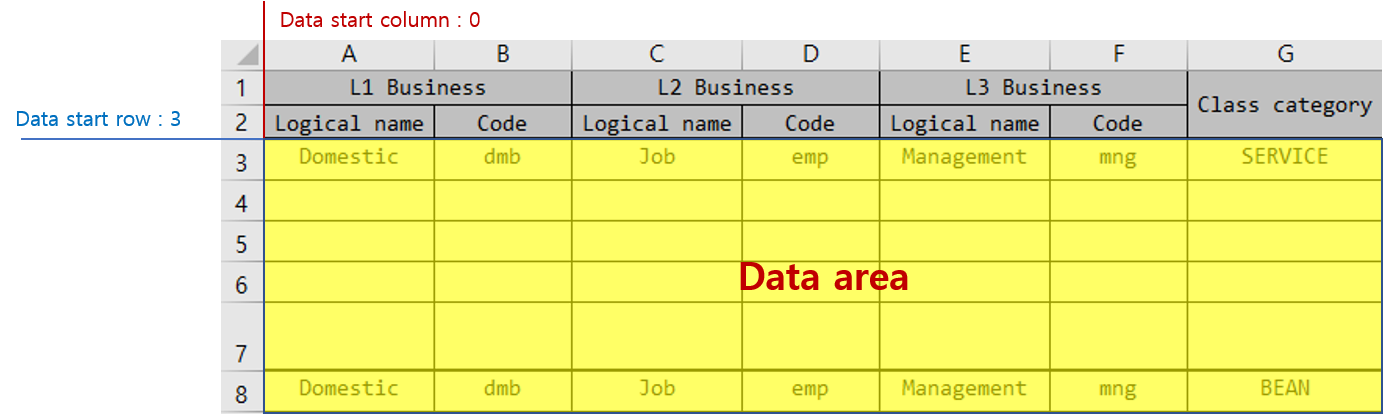
The default start position of the actual data area in each sheet is as follows:
-
Data start column: 0
-
Data start row: 3
If the Excel format needs to be changed depending on the development environment and the data start position must be moved, you can specify the data start area with the following options:
-
specifications.excel.componentProgramSpecifications.componentList.dataArea.columnNum:Specifies the starting column number of the data area in the Component Specifications sheet’s component list sheet. (zero-based)
-
Default: 0
-
-
specifications.excel.componentProgramSpecifications.componentList.dataArea.rowNum:Specifies the starting row number of the data area in the Component Specifications sheet’s component list sheet. (1-based)
-
Default: 3
-
-
specifications.excel.componentProgramSpecifications.ioList.dataArea.columnNum:Specifies the starting column number of the data area in the Component Specifications sheet’s IO List sheet. (zero-based)
-
Default: 0
-
-
specifications.excel.componentProgramSpecifications.ioList.dataArea.rowNum:Specifies the starting row number of the data area in the Component Specifications sheet’s IO List sheet. (1-based)
-
Default: 3
-
2. Component Program Specifications sheet
The Component Program Specifications sheet must be written as follows:
-
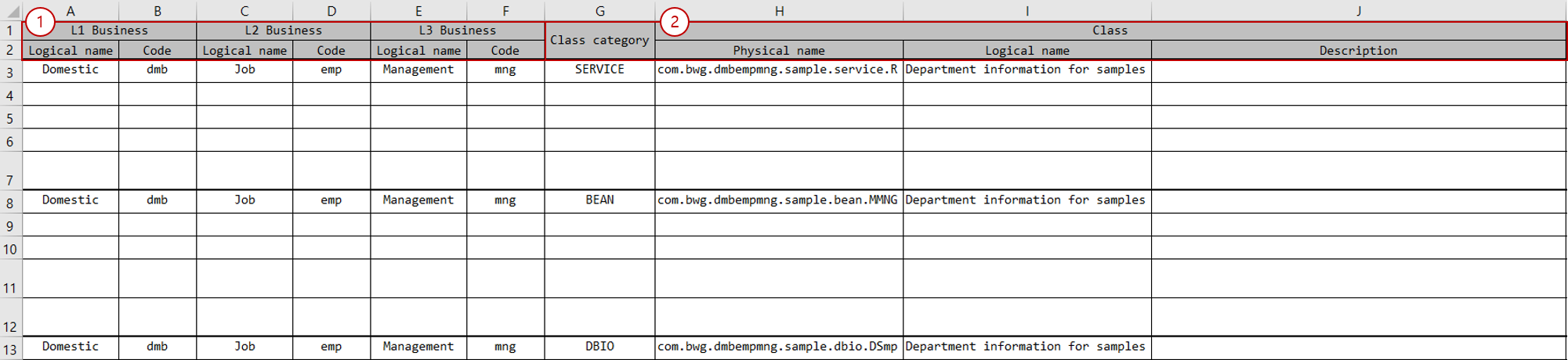
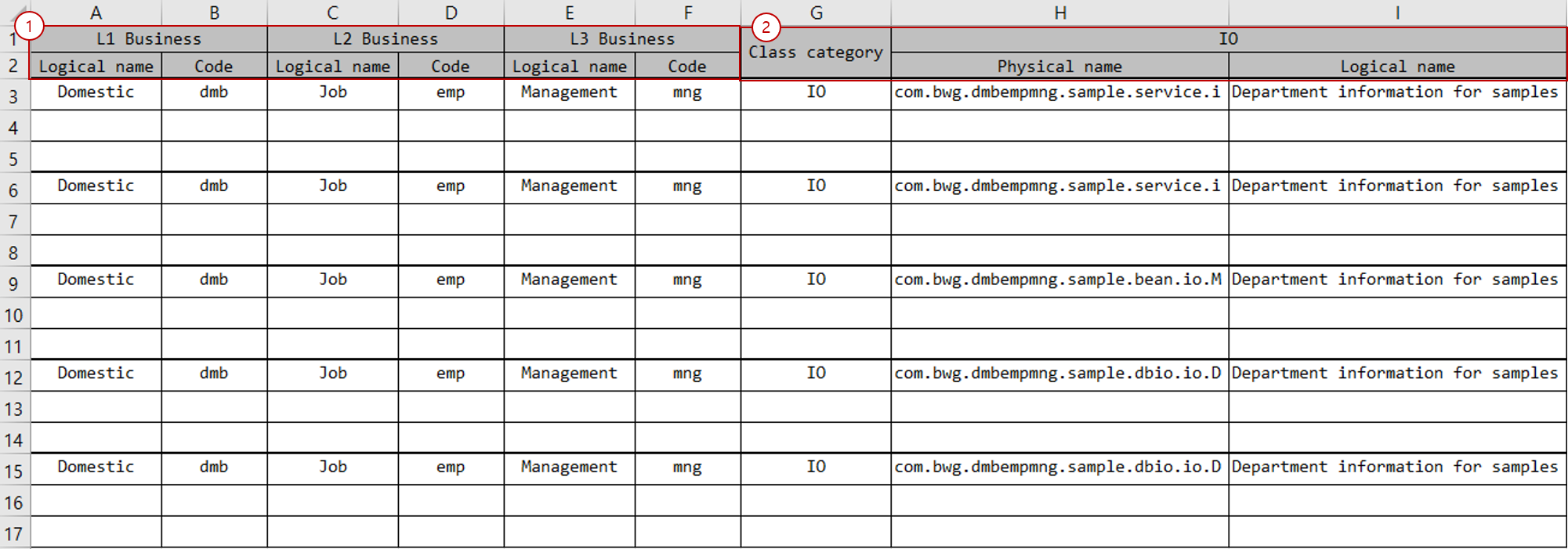
Business level code section: Write business level codes. Generally, business level codes are combined and used as a package name.
Attribute Description Logical name
Enter the logical name of the business level code.
Code
Enter the code of the business level code.
The number of business level codes may differ depending on the development environment. (Default: 3)
-
Class section: Classify Service, Bean, DBIO components and write class information.
Attribute Description Program type
Classifies the class. You can use
SERVICE,BEAN,DBIO, etc.Physical name
Enter the class name. If entered as a simple name, business level codes are combined and used as the package name. If entered as a full name, the package name is extracted from the full name and used.
Logical name
Enter the logical name of the class.
Description
Enter the description of the class.
-
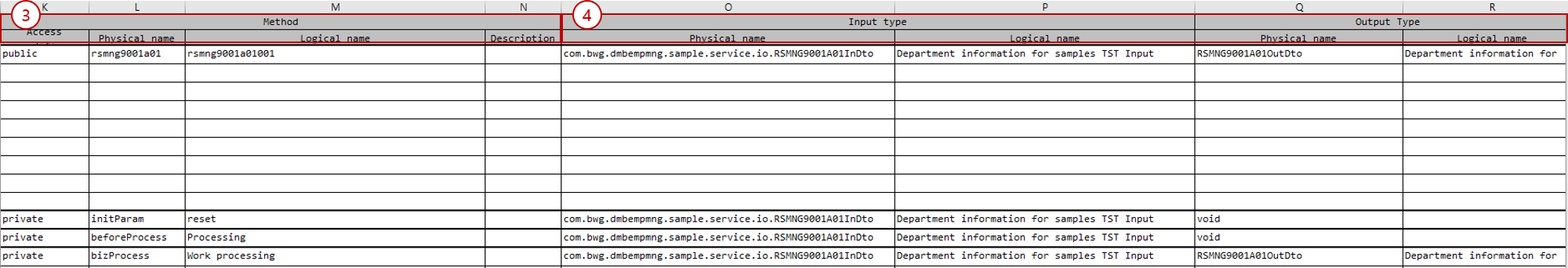
Operation/Method section: Write information on operations/methods.
Attribute Description Access modifier
Enter the access modifier of the operation/method. You can use
public,private,protected.Physical name
Enter the name of the operation/method.
Logical name
Enter the logical name of the operation/method.
Description
Enter the description of the operation/method.
-
Input/Output type section: Write the input/output types of operations/methods.
Attribute Description Input - Physical name
Enter the physical name of the input type. You can enter the class name of the IO or type names such as
int,String. If it is an IO type and entered as a simple name, business level codes are combined and used as the package name.Input - Logical name
If the input type is IO, enter the logical name of the IO.
Output - Physical name
Enter the physical name of the output type. You can enter the class name of the IO or type names such as
int,String. If it is an IO type and entered as a simple name, business level codes are combined and used as the package name.Output - Logical name
If the output type is IO, use the logical name of the IO.
-
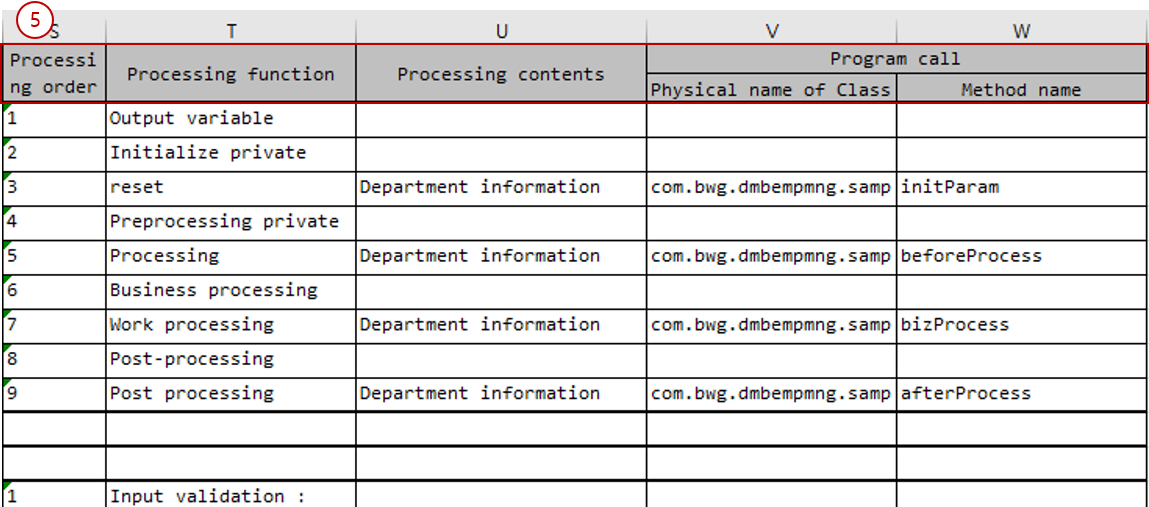
Program processing order section: Write the contents to be processed inside the operation/method. If there are multiple processing contents, write them over multiple rows.
Attribute Description Processing order
Enter the processing order of the processing function as a numeric value.
Processing function
Enter a value that can representatively describe the content to be processed.
Processing contents
Enter detailed content of what to process.
Physical name of Class
Enter the full name of the component (class) to be called.
Method name
Enter the full name of the operation (method, SQL ID) of the component (class) to be called.
3. IO List sheet
The IO List sheet must be written as follows:
-
Business level code section: Write business level codes. Generally, business level codes are combined and used as a package name.
Attribute Description Logical name
Enter the logical name of the business level code.
Code
Enter the code of the business level code.
The number of business level codes may differ depending on the development environment. (Default: 3)
-
Class section: Write information for IO.
Attribute Description Class category
Enter the type of component in which the IO will be used. You can use
SERVICE,BEAN,DBIO, etc.Physical name
Enter the name of the IO. This becomes the actual file name. If entered as a simple name, business level codes are combined and used as the package name. If entered as a full name, the package name is extracted from the full name and used.
Logical name
Enter the logical name of the IO.
-
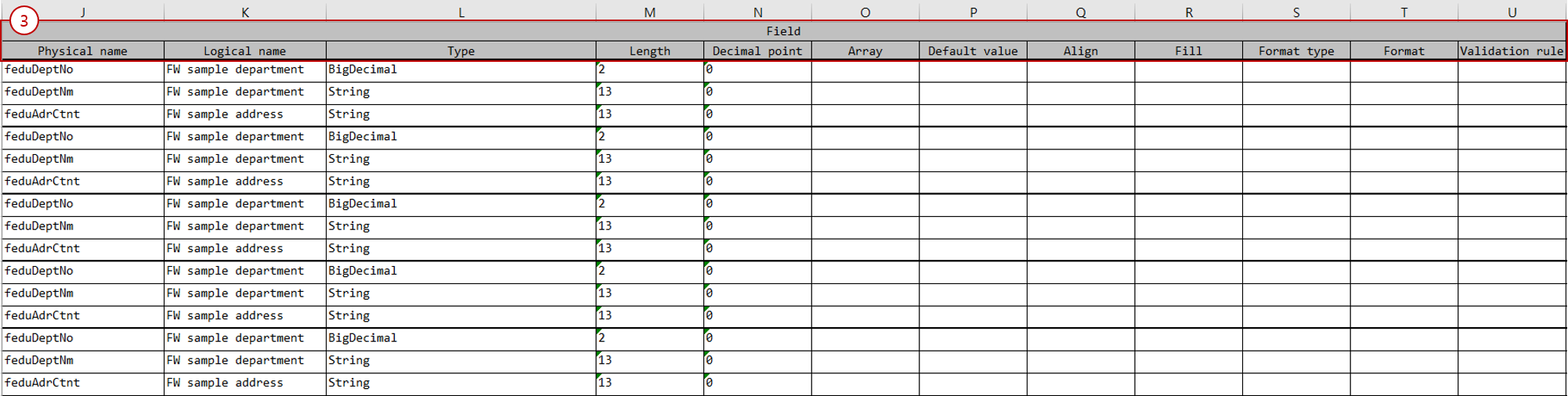
Field section: Write field information to be used in IO.
Attribute Description Physical name
Enter the name of the field. Java standard variable names can be used.
Logical name
Enter the logical name of the field.
Type
Enter the type of the field. Types such as
String,Integer,Long,Boolean,BigDecimal,Datecan be used.Length
Enter the length of the field. The length attribute is applied to Fixed-Length Data.
Decimal point
Enter the valid decimal places of the field. The valid decimal places attribute is applied to Fixed-Length Data.
Array
If the field needs to be used as an array (
List), enter a numeric value or the name of a field (Integertype) that represents the array count.Default value
Enter the default value of the field.
Align
Enter the alignment method of the data. You can use
left,right. The alignment attribute is applied to Fixed-Length Data.Fill
Enter the character to fill the remaining space of the data. You can use
*. The padding attribute is applied to Fixed-Length Data.Format type
Enter the format type of the data. You can use
date,currency,masking.Format
Enter the data format that matches the format type. For example,
yyyyMMdd,#,###.00.Validation rule
Enter the ID of the rule to validate the data.
For detailed IO field attributes, refer to the IO editor chapter.