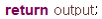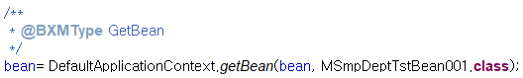Flow Viewer
The flow viewer is supported so that completed Java sources can be checked through the GUI. Through this editor, you can intuitively check the source and easily compare the design and implementation deliverables.
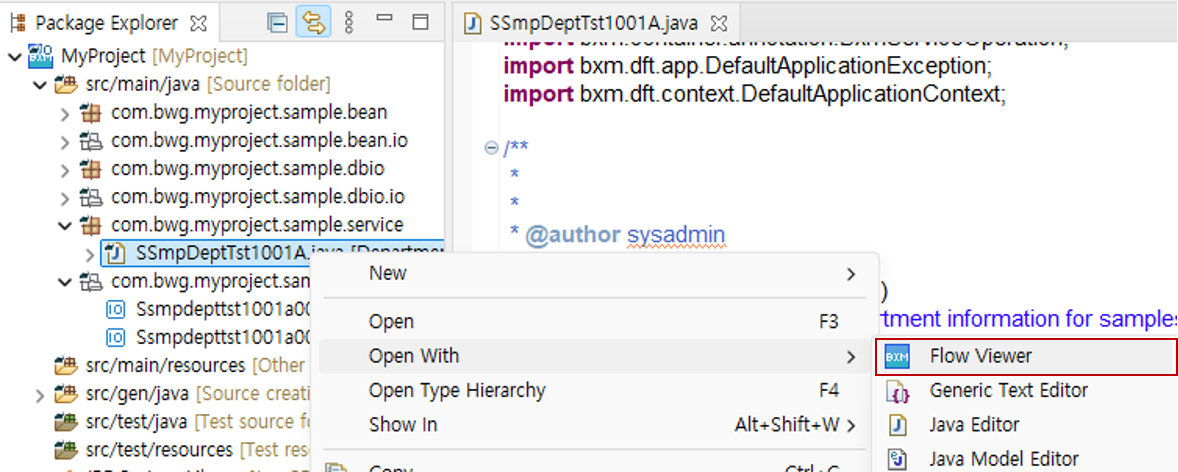
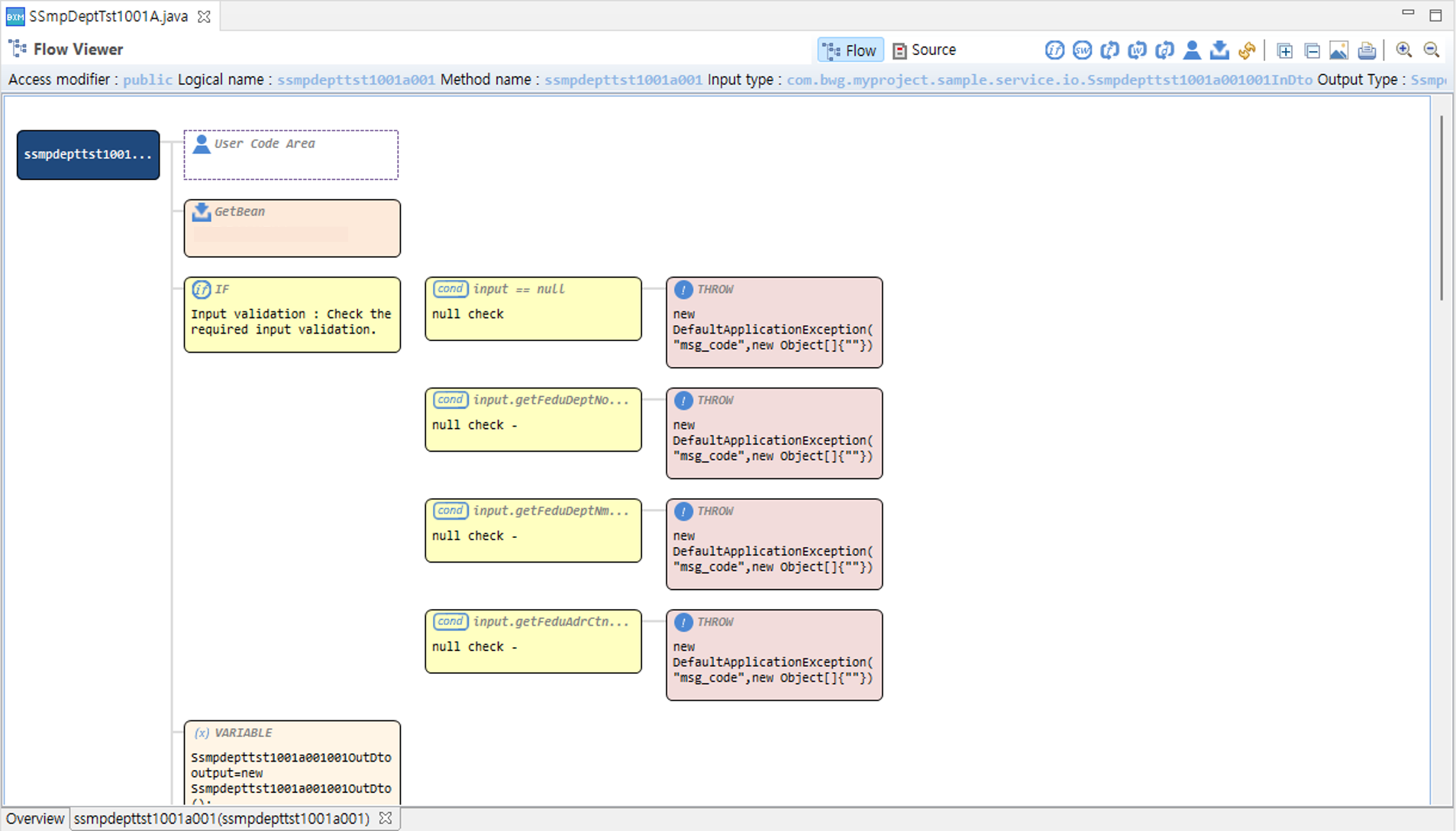
The flow viewer is executed as shown in the figure below.
-
Package Explorer → select the desired Java source → right-click → Open With → click 'Flow Viewer'.
1. Layout
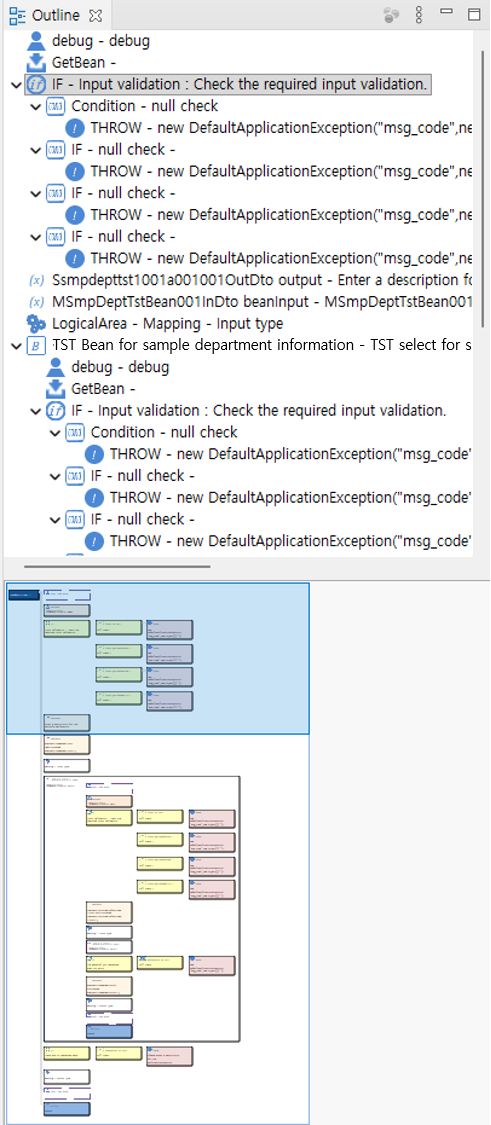
The flow viewer consists of two pages.
-
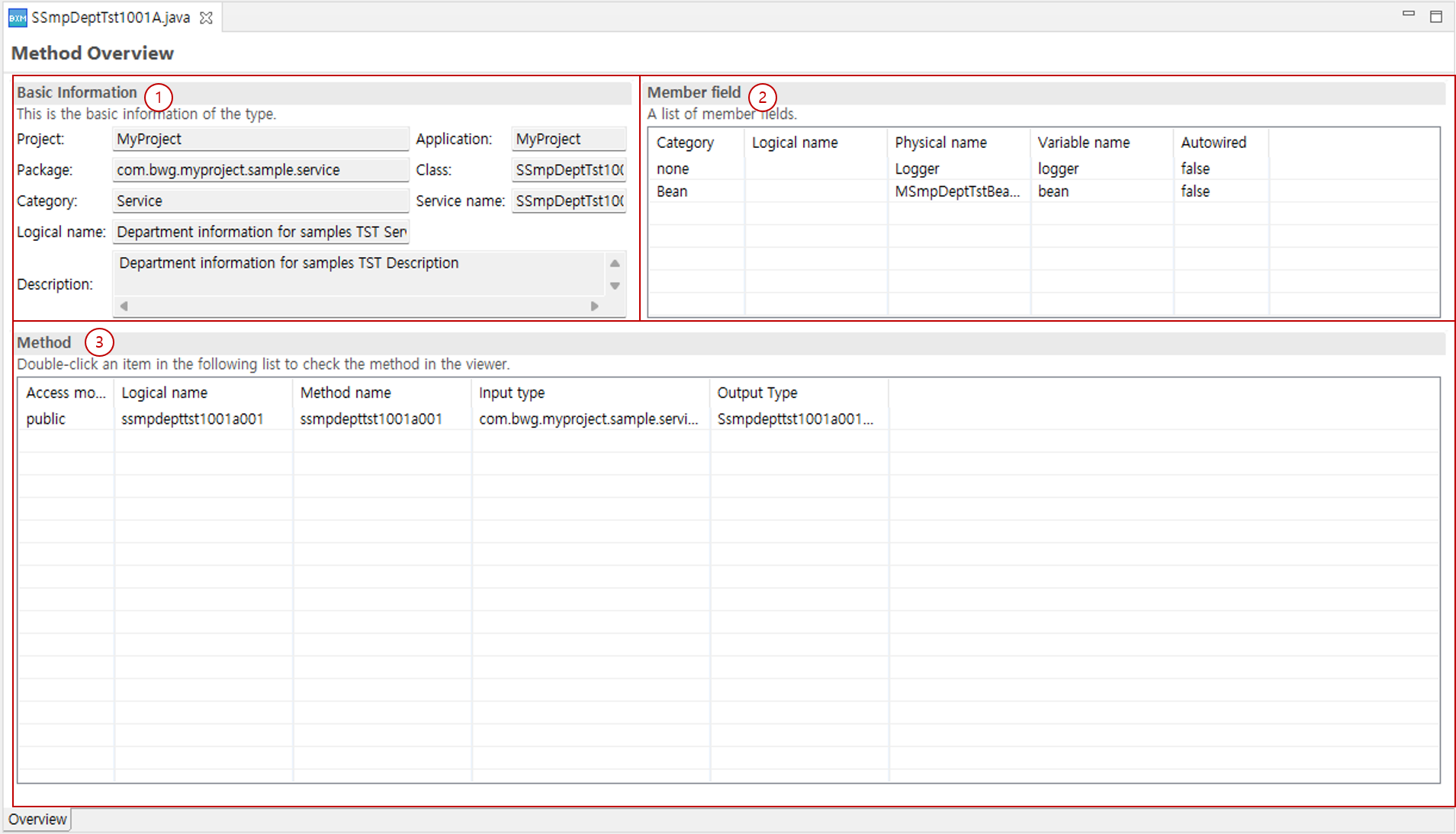
Overview page: Shows basic information about the class.
-
Flow page: Shows the flow and source of the class.
2. Overview
On the overview page, you can check basic class information, member fields, and operation/method information of service/business modules.
The overview page consists of the following three parts.
-
Basic information: You can check the basic information of the created class.
-
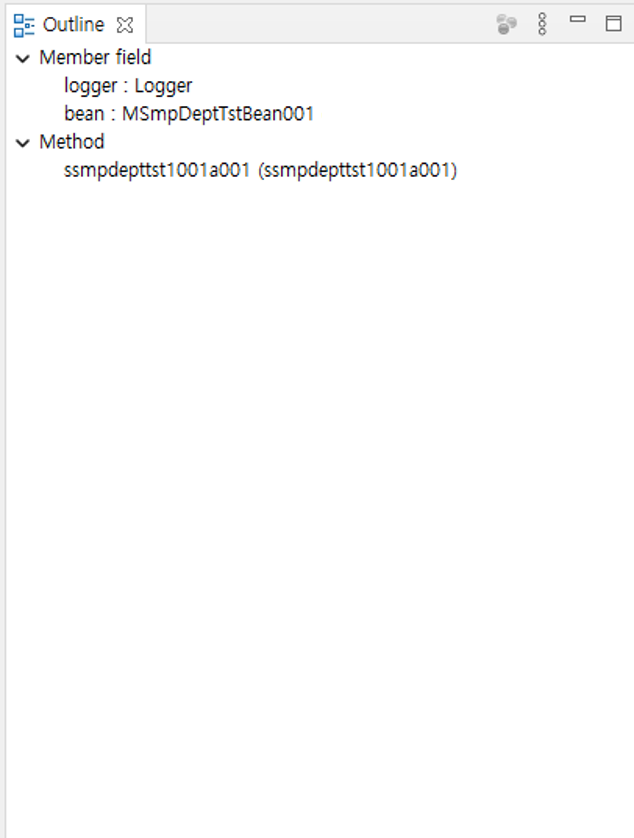
Member fields: You can check the list of member fields that the class has.
-
Methods: You can check the list of methods that the class has.
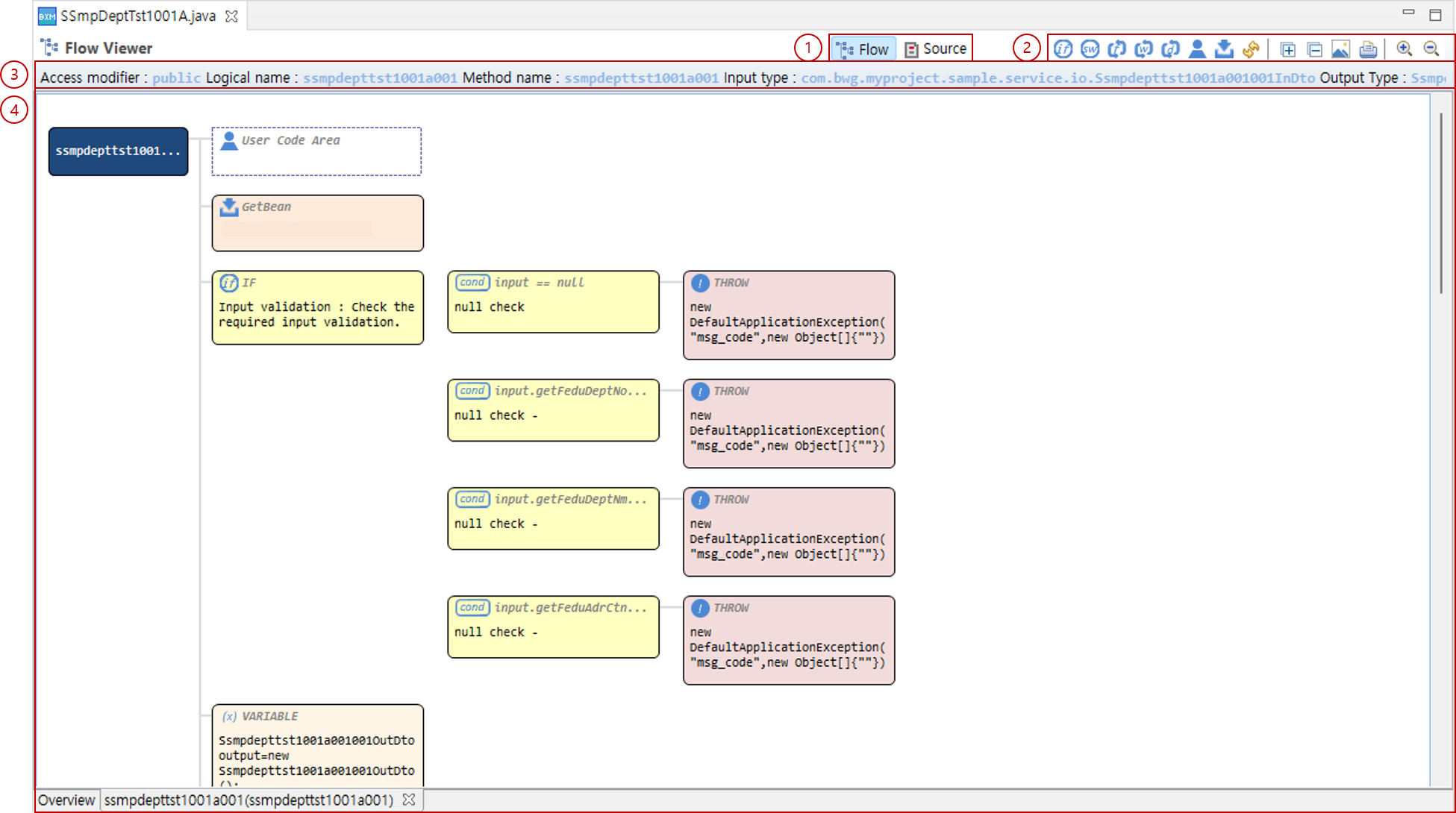
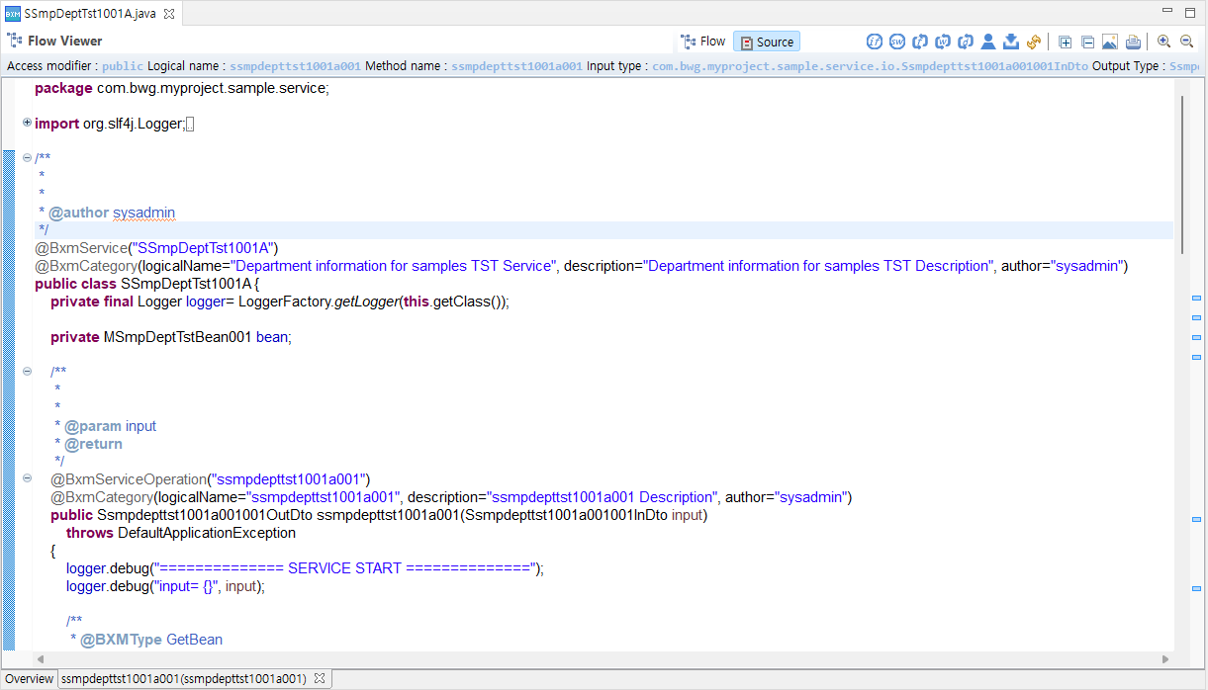
3. Flow page
On the flow page, the flow of the source code executed by the method is displayed.
The flow page consists of the following four parts.
-
Top tabs: Through the Flow/Source tabs, you can check the flowchart and source code for the source.
-
Top toolbar: Menus for convenience are located at the top of the workspace.
-
Show/Hide nodes: Provides the ability to hide specific nodes (if, switch, for, while, do-while, user code area, getBean) in the workspace.
-
Export image: You can export the flow created in the workspace as an image.
-
Print: You can print the flow created in the workspace and output it as a printout.
-
Expand/Collapse all nodes: Provides expand/collapse functionality for all nodes.
-
Zoom: You can adjust the zoom level of the workspace view.
-
-
Basic information: You can simply check the access modifier, logical name, method name, and input/output types of the method.
-
Viewer: Depending on the top tab, you can check the flow/source code.
3.1. Nodes
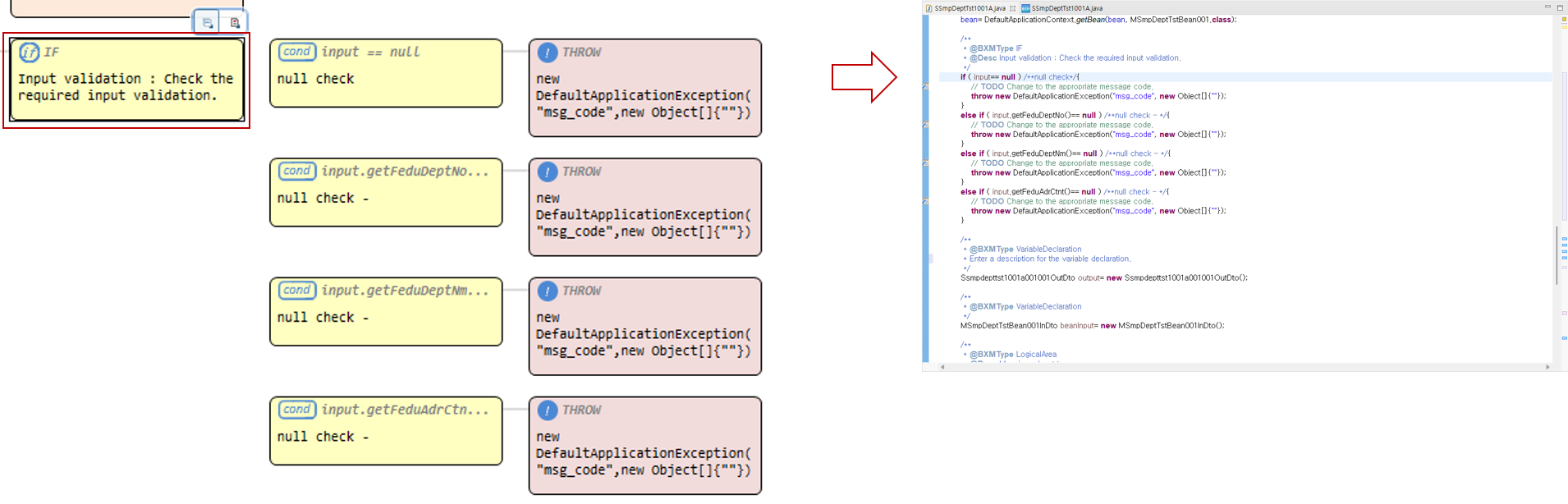
In the flow designer, source code is displayed in units of nodes. The source code must be written in a predefined format so that the flow designer can recognize it and represent it as nodes.
3.1.1. Relationship between nodes and source code
The following table explains the relationship between nodes and source code.
| Node image | Node name | Node description | Source code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Logical area |
Divides source code into logical units. Generally used when grouping other nodes. |
|
|
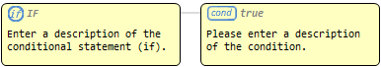
Conditional statement |
Node corresponding to if(condition). |
|
|
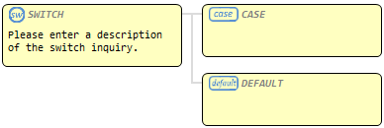
Conditional statement |
Node corresponding to switch. |
|
|
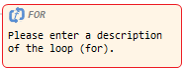
For loop |
Node corresponding to for(initialization;condition;increment). |
|
|
For Each loop |
Node corresponding to for(parameter : iterator). |
|
|
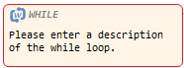
While loop |
Node corresponding to while(condition). |
|
|
Do While loop |
Node corresponding to do{…} while(condition). |
|
|
Bean module call |
Node that calls a method defined in a bean module. |
|
|
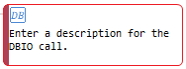
DBIO module call |
Node that calls a method defined in a DBIO module. |
|
|
Service Executor call |
Node that calls a service through the provided service Executor. |
|
|
Variable declaration |
If a variable to be expressed in the flow is required, it can be declared through a variable declaration node. |
|
|
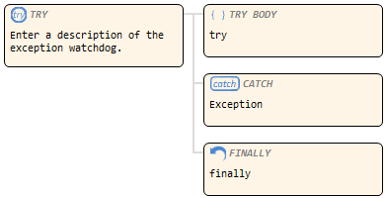
Exception monitoring |
Node corresponding to try/catch/finally. |
|
|
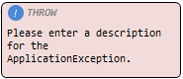
Throw application exception |
Node that throws an application exception class. |
|
|
Return |
Node corresponding to return. |
|
|
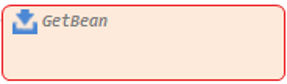
GetBean |
Node corresponding to the code that initializes the object of the member field of the module before the method of the business/DBIO module is called. However, if the member field is defined as |
|
|
User code area |
All code except the source code listed above is displayed as a user code area. |
|
3.1.2. Collapse nodes
Nodes that have child nodes can hide the child nodes through the Collapse function.