Parallel Processing of Batch Jobs
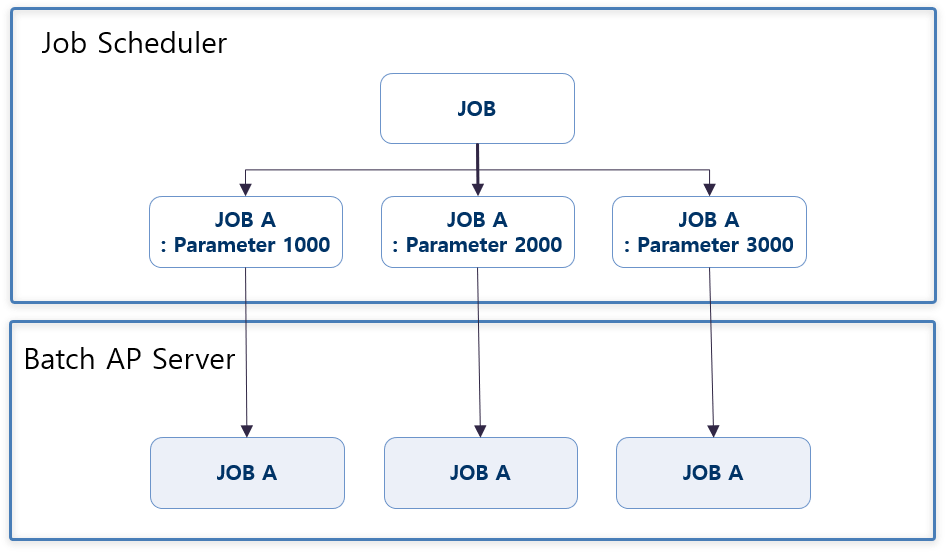
Parallel processing of batch can be performed by job parallel processing, where the scheduler invokes the same batch Job with different parameter values, and by step parallel processing, where multiple Steps within a single batch Job are executed simultaneously.
1. Parallel Processing of Batch Jobs
This method handles the simultaneous invocation of the same Job with different parameter values from the scheduler.
In the framework, a Job Instance is created as a combination of the batch Job ID and execution parameters (JobParameter), so that multiple instances of the same batch Job can be executed.
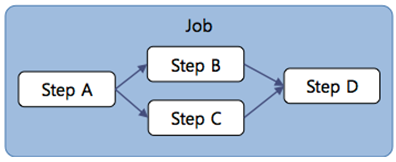
2. Parallel Step Processing Within a Single Batch Parallel Job
Some unit Steps can be processed in parallel regardless of order by defining the Step flow so that they are executed simultaneously.
(Refer to 'Chapter 4. Step Execution Flow')
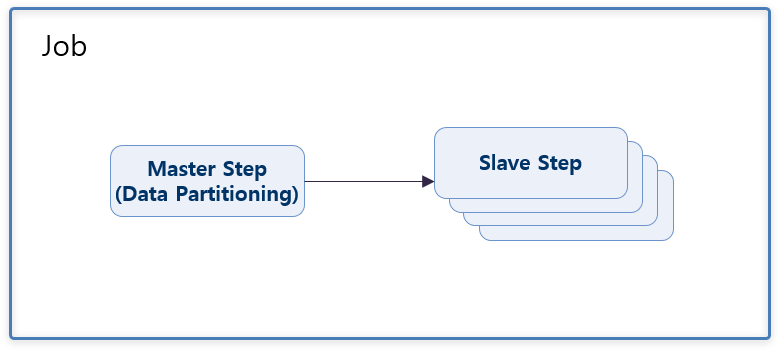
3. Data Partition Processing
This method divides the data to be processed and processes the partitioned data in parallel with multiple threads simultaneously.
In the batch job xml, the Master Step must be defined with the partition element, and the Slave Step must be located outside the Job flow.
The number of parallel processes is configured by the value of the grid-size attribute of the handler element. This value is passed as a parameter to the partition method of the Partitioner class.
<job id="JSmpPartitioning" xmlns="http://www.bankwareglobal.com/schema/batchex">
<step id="JSmpPartitioning100" parent="parentStep">
<partition partitioner="MSmpPartitioning" step="JSmpPartitioning200">
<handler grid-size="3"/>
</partition>
</step>
</job>
<step id="JSmpPartitioning200" parent="parentStep" xmlns="http://www.bankwareglobal.com/schema/batchex">
<tasklet>
<chunk reader="MSmpPartitioningDBToFixedBtch" processor="MSmpPartitioningDBToFixedBtch" writer="WJSmpPartitioning200"/>
</tasklet>
</step>Partitioner class: Implements the logic to check and distribute the data to be partitioned.
(It delivers the data to be partitioned to the next Step using ExecutionContext.)
@BxmBean("MSmpPartitioning")
@Scope("step")
@BxmCategory(logicalName = "MSmpPartitioning")
public class MSmpPartitioning implements Partitioner{
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
@BxmCategory(logicalName = "MSmpPartitioning")
public Map<String, ExecutionContext> partition(int gridSize)
{
/**
* Map for delivering the ExecutionContext information of Steps distributed by Partition
* - Steps are executed in parallel as many times as the size of the Map. (Usually, the received gridSize value is defined as the size of the Map.)
*/
Map<String, ExecutionContext> executionContextMap = new HashMap<String, ExecutionContext>();
/**
* Set ExecutionContext in the Map as many times as gridSize.
*/
for(int ix = 1; ix <= gridSize; ix++)
{
/**
* Set ExecutionContext values
* - Set the values to be processed by Partitioning.
*/
ExecutionContext executionContext = new ExecutionContext();
executionContext.put("deptNo", ix * 10);
/**
* Set the ExecutionContext value with the Partition Id as the key.
*/
executionContextMap.put("id_" + ix, executionContext);
}
return executionContextMap;
}
}In the Slave Step, the target range is checked from the received ExecutionContext.
@BxmCategory(logicalName = "open : Sample employee information Iterator processing")
public void open(ExecutionContext executionContext) throws ItemStreamException
{
if(dSmpEmpTst001 == null) {
dSmpEmpTst001 = DefaultApplicationContext.getBean(DSmpEmpTst001.class);
}
/**
* Get batch input parameter "deptNo"
*/
int deptNo = executionContext.getInt("deptNo");
/**
* Retrieves sample employee information as an Iterator for the input "deptNo".
*/
DSmpEmpTst001selectList01InDto inDto = new DSmpEmpTst001selectList01InDto();
inDto.setFeduDeptNo(deptNo);
iterator = dSmpEmpTst001.selectList01(inDto).iterator();
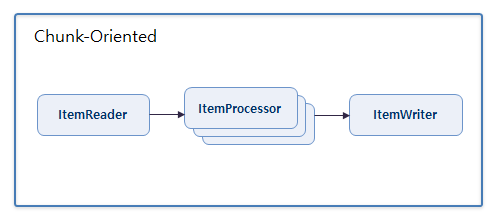
}4. Parallel Processing of ItemProcessor
This method synchronously processes ItemReader and ItemWriter, while only ItemProcessor is processed asynchronously and in parallel.
※ Note: For member variables used in the ItemProcessor that is processed in parallel, be sure to use Thread Safe types (such as AtomicInteger, AtomicReference, etc.). Also, since the Select of ItemProcessor processed in parallel uses a separate Connection for faster processing speed, it may not be executed normally in the following cases:
-
When FOR UPDATE is used (Oracle)
-
When data processed as C/U/D inside ItemProcessor is re-queried
<job id="JSmpAsynItemProcessor" xmlns="http://www.bankwareglobal.com/schema/batchex">
<step id="JSmpAsynItemProcessor100" parent="parentStep">
<tasklet tm-datasource="MainDS">
<chunk reader="MSmpTestChunkedBean" processor="AsyncMSmpTestChunkedBean" writer="MSmpTestChunkedBean"/>
</tasklet>
</step>
</job>
<bean id="AsyncMSmpTestChunkedBean" parent="AsyncItem">
<property name="processor" ref="MSmpTestChunkedBean"/> <!-- ItemProcessor Bean configuration -->
<property name="size" value="5"/> <!-- Number of Threads -->
</bean>