Batch Application Naming Rules
2. Batch Application
BXM divides the application units for batch based on different management entities and units that can minimize function calls between applications. Applications are created through the 'Bxm Application' menu in Studio.
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
Composition |
L1 code + L2 code + L3 code + Batch |
Example of Application |
BxmDftSmpBatch |
Basic Rules |
|
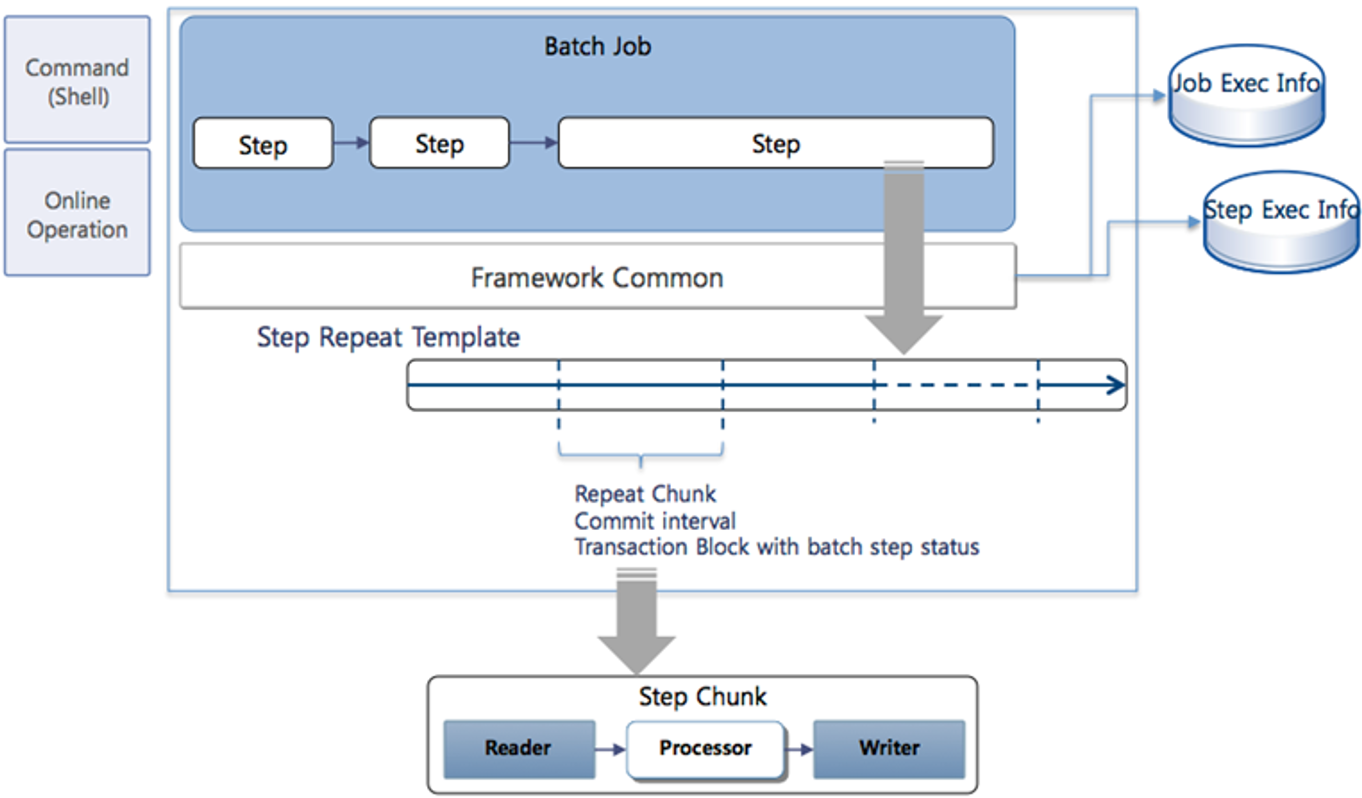
3. Job
A Job is the logical unit of a batch business processing process, consists of multiple Steps, and becomes the execution unit of batch business. The name of a Job is written as follows.
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
Composition |
J + L3 code + Unique identification ID |
Example |
JSmpAccountTaxSum JSmpTotalProc |
Basic Rules |
|
Example |
|
4. Step
A Step is the minimum execution business unit of a batch. One Job has 1 to N Steps, and Steps are executed sequentially. When Steps are not executed sequentially but processed in Parallel Processing, use Split, which is a type of Step. The names of Steps and Splits are written as follows.
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
Composition |
JOB ID + 1-digit step serial number + 2-digit split serial number If there are only Steps, the numbers increase in the order of 100, 200. |
Example |
JSmpAccountTaxSum100 JSmpAccountTaxSum101 |
Basic Rules |
|
Example |
|
5. Job Configuration File
The name of the file that sets the configuration of a Job is written as follows.
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
Composition |
JOB ID + .xml |
Example |
JSmpAccountTaxSum.xml JSmpTotalProc.xml |
Basic Rules |
|