New Batch Job
This section describes the functions of the New Batch Job wizard.
Depending on the batch Job type (chunked, tasklet) and the batch Reader/Writer type (File, DB, etc.), it automatically generates batch bean, DBIO, and Job Config files.
There are two main types of batch Jobs.
| Batch Job Type | Description |
|---|---|
Tasklet |
Used for simple DB CRUD operations or batches that must be committed/rolled back at once. |
Chunked |
Defines and uses an |
Run the New Batch Job wizard as shown in the figure below.
-
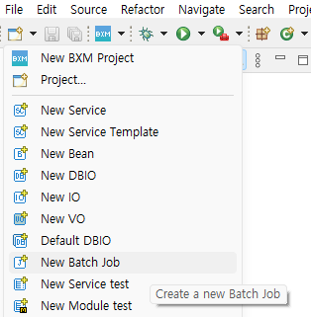
Click New → 'New Batch Job' in the Quick menu at the top left.
1. Tasklet
Used for simple DB CRUD operations or batches that must be committed/rolled back at once.
-
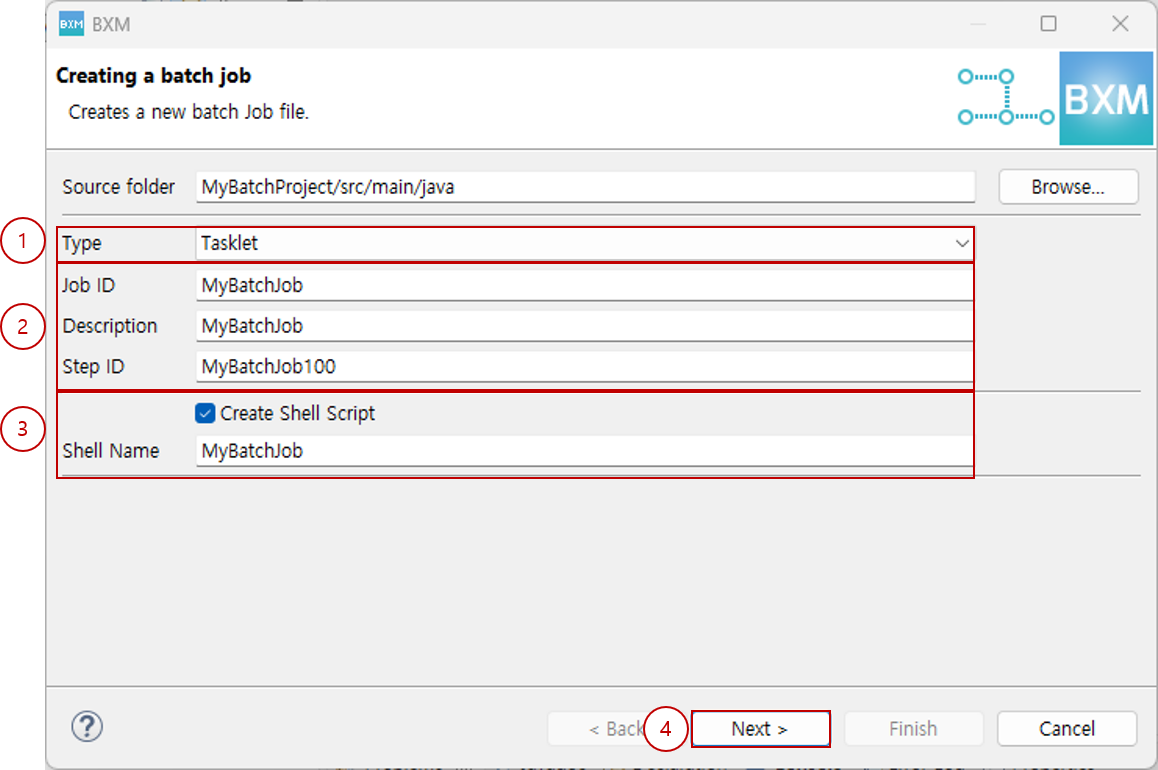
Select the Tasklet type, enter the job ID, and click Next.
At this time, the step ID and shell name are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Select Tasklet type
(2) Enter Job ID and Step ID
(3) Select whether to generate a shell script and enter the shell name
(4) Click Next -
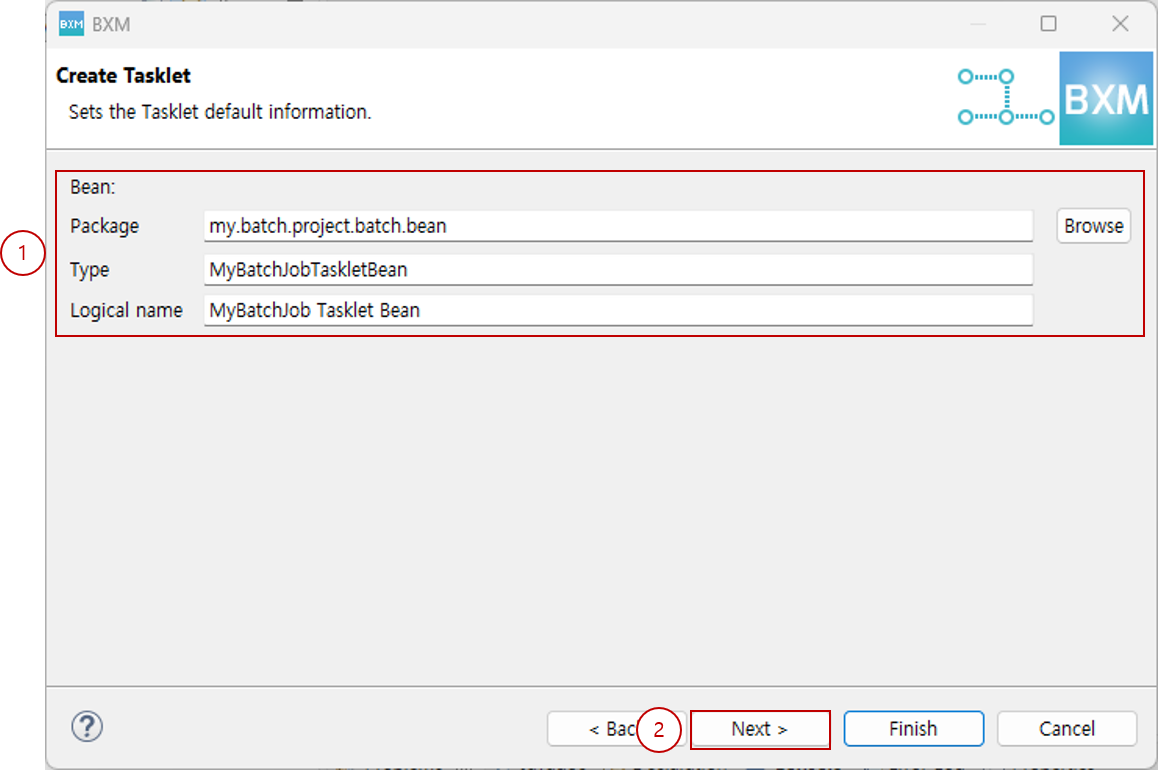
Enter the package, type, and logical name.
At this time, the package, type, and logical name are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Enter the package, type, and logical name
(2) Click Next
2. Chunk
Defines and uses an ItemReader that receives input one item at a time from a DB or file, an ItemProcessor that processes the business logic one item at a time, and an ItemWriter that outputs the result.
-
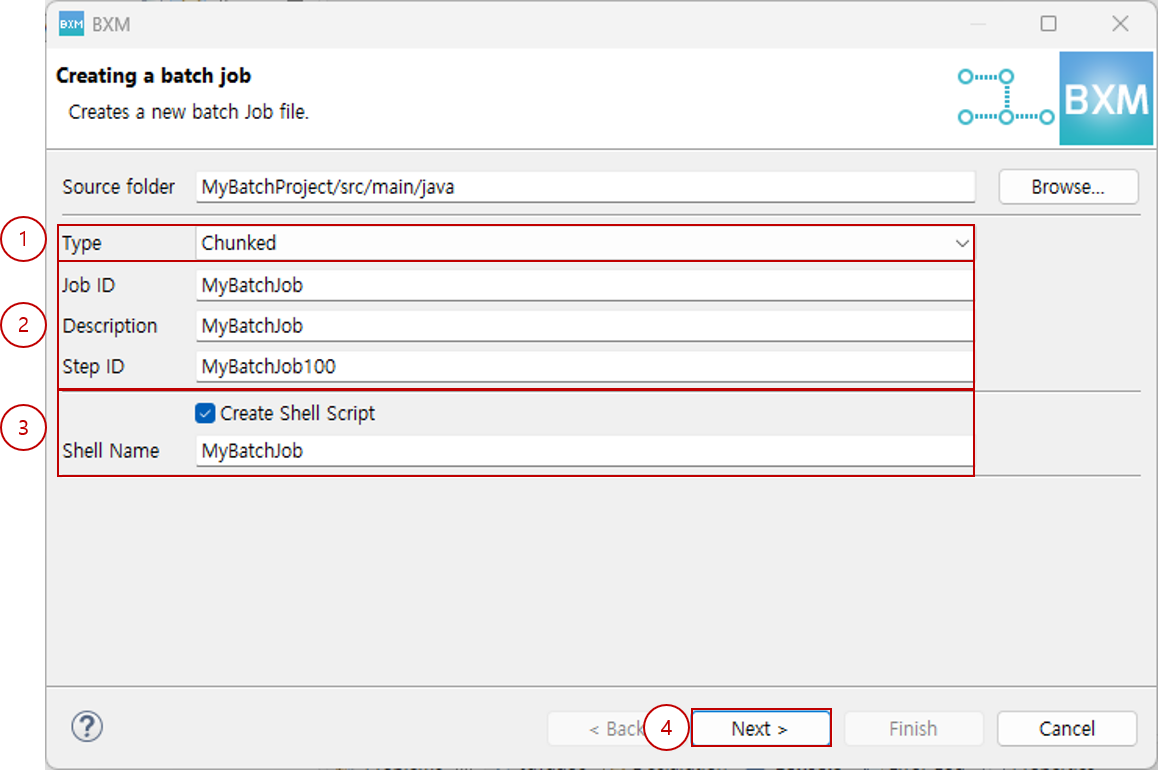
Select the Chunked type, enter the Job ID, and click Next.
At this time, the step ID and shell name are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Select Chunked type
(2) Enter Job ID and Step ID
(3) Select whether to generate a shell script and enter the shell name
(4) Click Next -
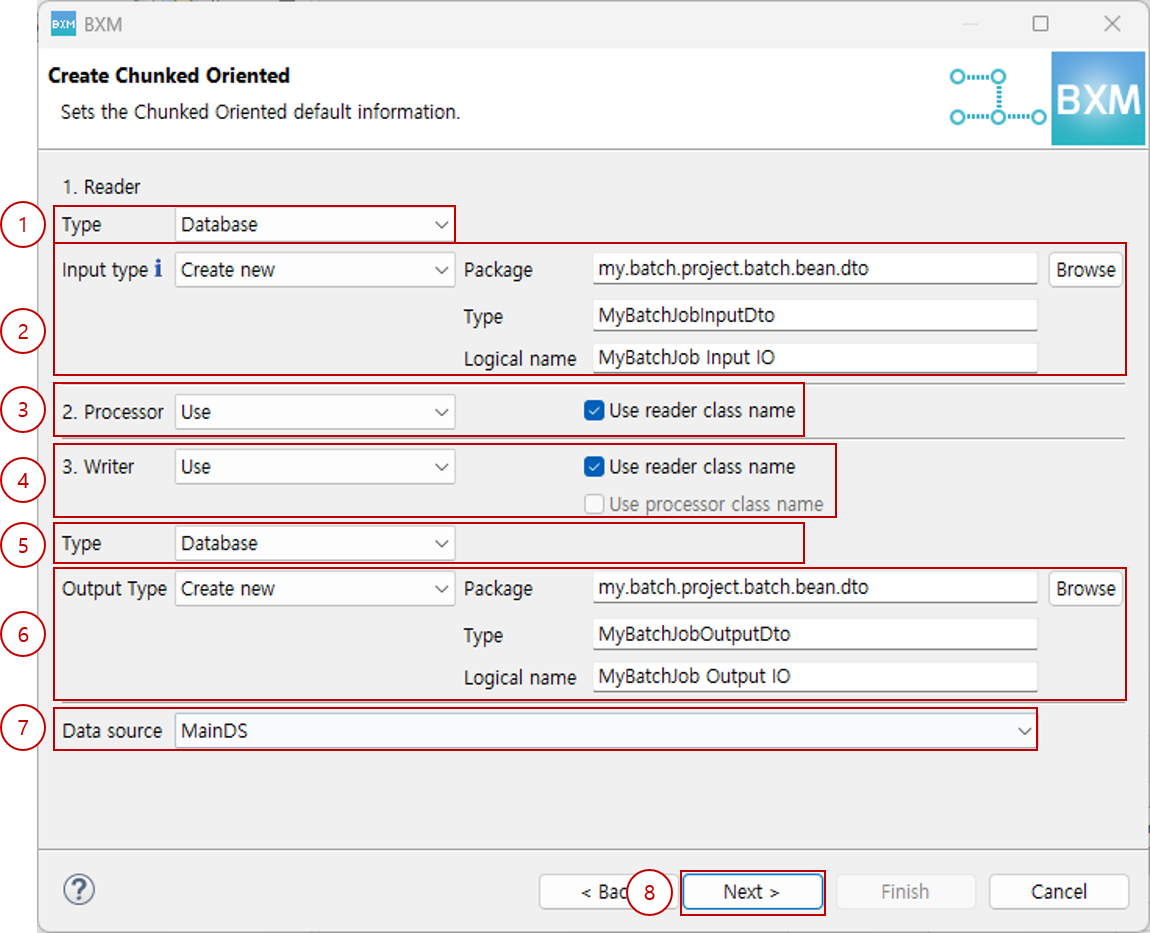
Select the type, input package, type, and logical name of the
Reader; select whether to use theProcessor; select whether to use theWriter, its type, output package, type, logical name, and data source; then click Next.At this time, the package, type, and logical name are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Select
ReadertypeReader Type Description Database
Used when querying batch target data using DBIO.
Fixed
Used when reading a fixed-length file.
Delimited
Used when reading a file defined with delimiters.
MultiType Fixed
Used when reading a file with a Header/Body/Footer structure of fixed length.
MultiType Delimited
Used when reading a file with a Header/Body/Footer structure defined by delimiters.
Variable
Used when reading a file line by line in string format. (IO is not defined because it is passed to
ItemProcessoras aString.)File Read Source(Fixed)
Used when reading a fixed-length file implemented in source code.
File Read Source(Delimited)
Used when reading a file defined with delimiters implemented in source code.
(2) Enter input type package, type, and logical name
(3) Select whether to useProcessorand its options
(4) Select whether to useWriterand its typeWriter Type Description Database
Used when inserting/updating/deleting result data using DBIO.
Fixed
Used when writing a fixed-length file.
Delimited
Used when writing a file defined with delimiters.
MultiType Fixed
Used when writing a file with a Header/Body/Footer structure of fixed length.
MultiType Delimited
Used when writing a file with a Header/Body/Footer structure defined by delimiters.
Variable
Used when writing a file line by line in string format.
File Read Source(Fixed)
Used when writing a fixed-length file implemented in source code.
File Read Source(Delimited)
Used when writing a file defined with delimiters implemented in source code.
(5) Enter output type package, type, and logical name
(6) Select data source
(7) Click Next
2.1. Definition by Reader Type
Enter the required information for each Reader type.
2.1.1. Database Type
-
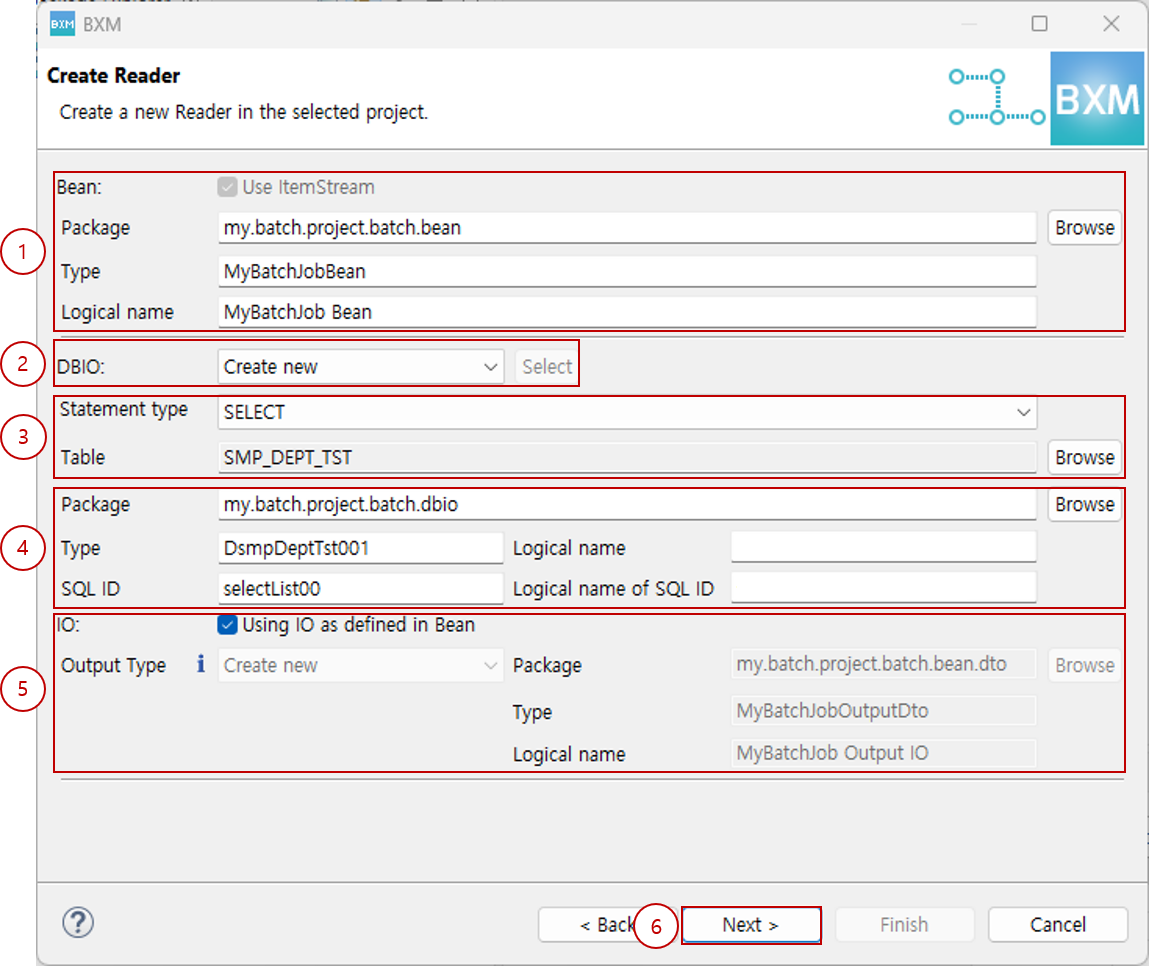
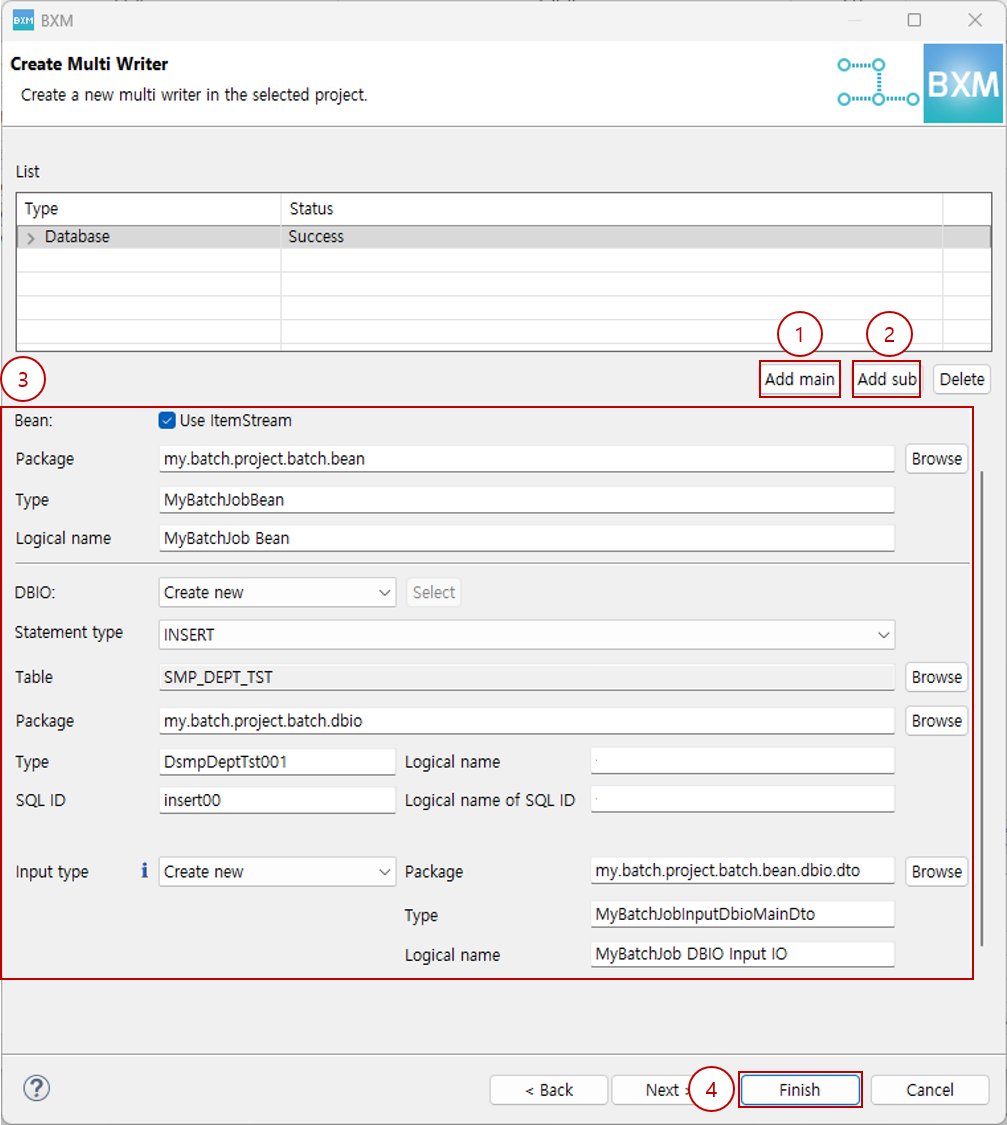
Select the Bean package, type, logical name, statement type, and the desired table, then click Next.
At this time, all resource names are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Enter the Bean package, type, and logical name
(2) Select DBIO generation method (Create new, Select existing DBIO)
(3) Select statement type and table
(4) Enter DBIO package, type, logical name, SQL ID, and logical name of SQL ID
(5) Enter output type package, type, and logical name
(6) Click Next
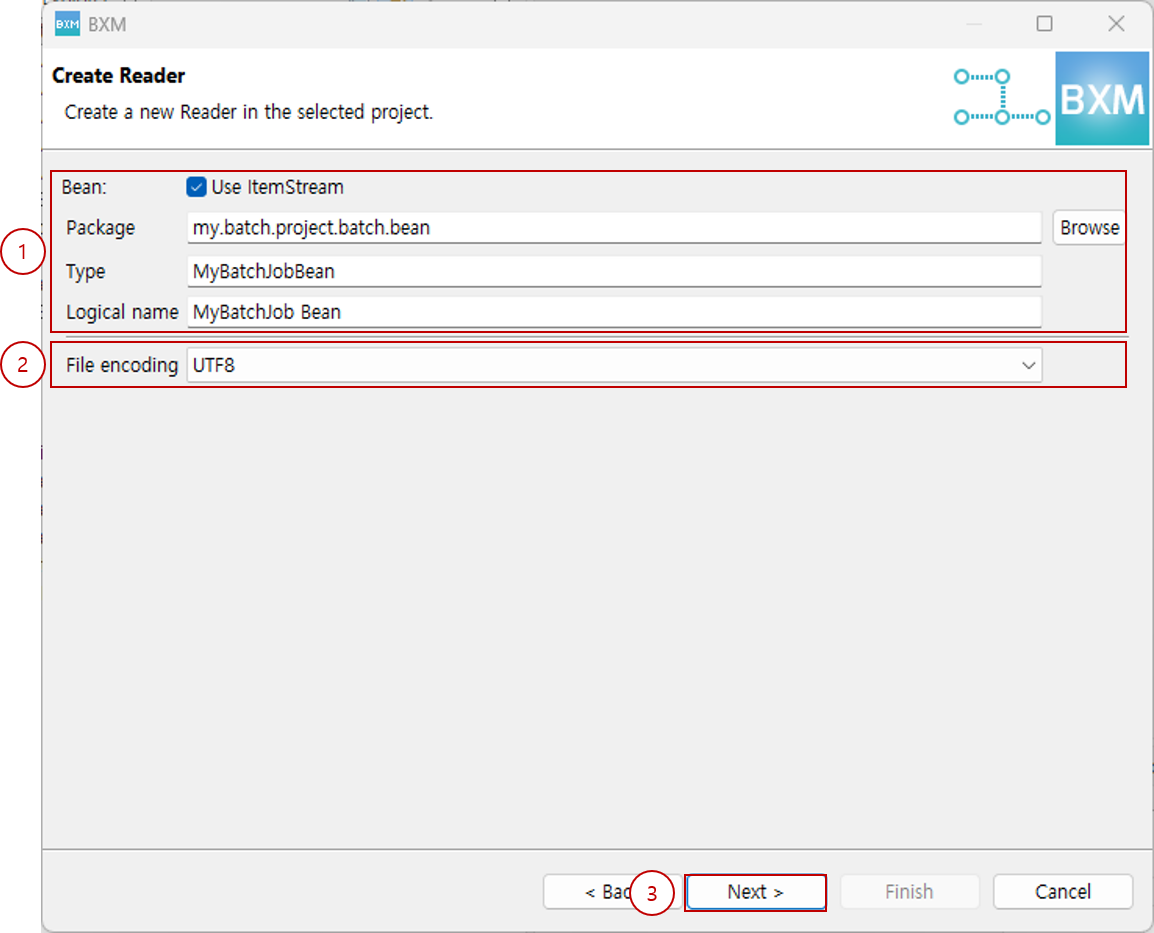
2.1.2. Fixed, MultiType Fixed, Variable Types
-
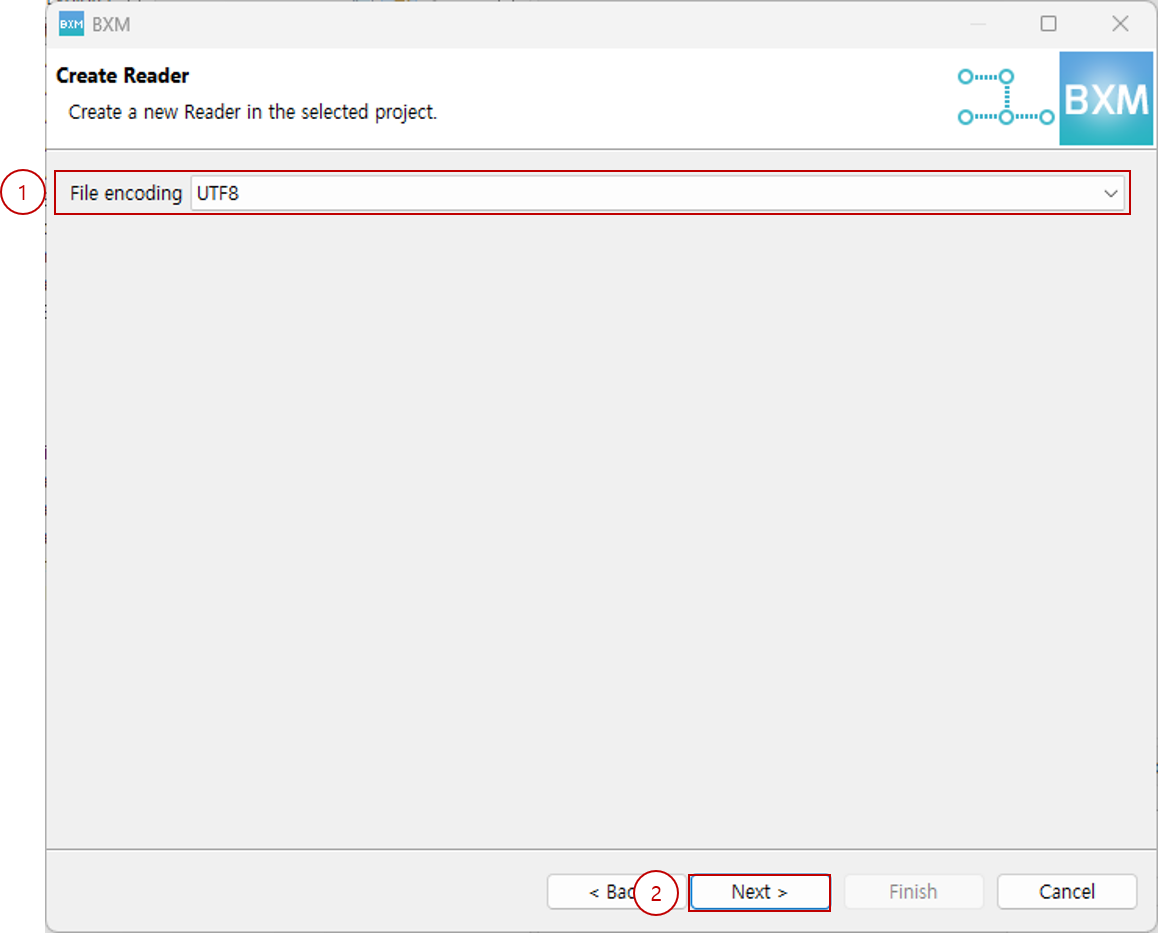
Select file encoding and click Next.
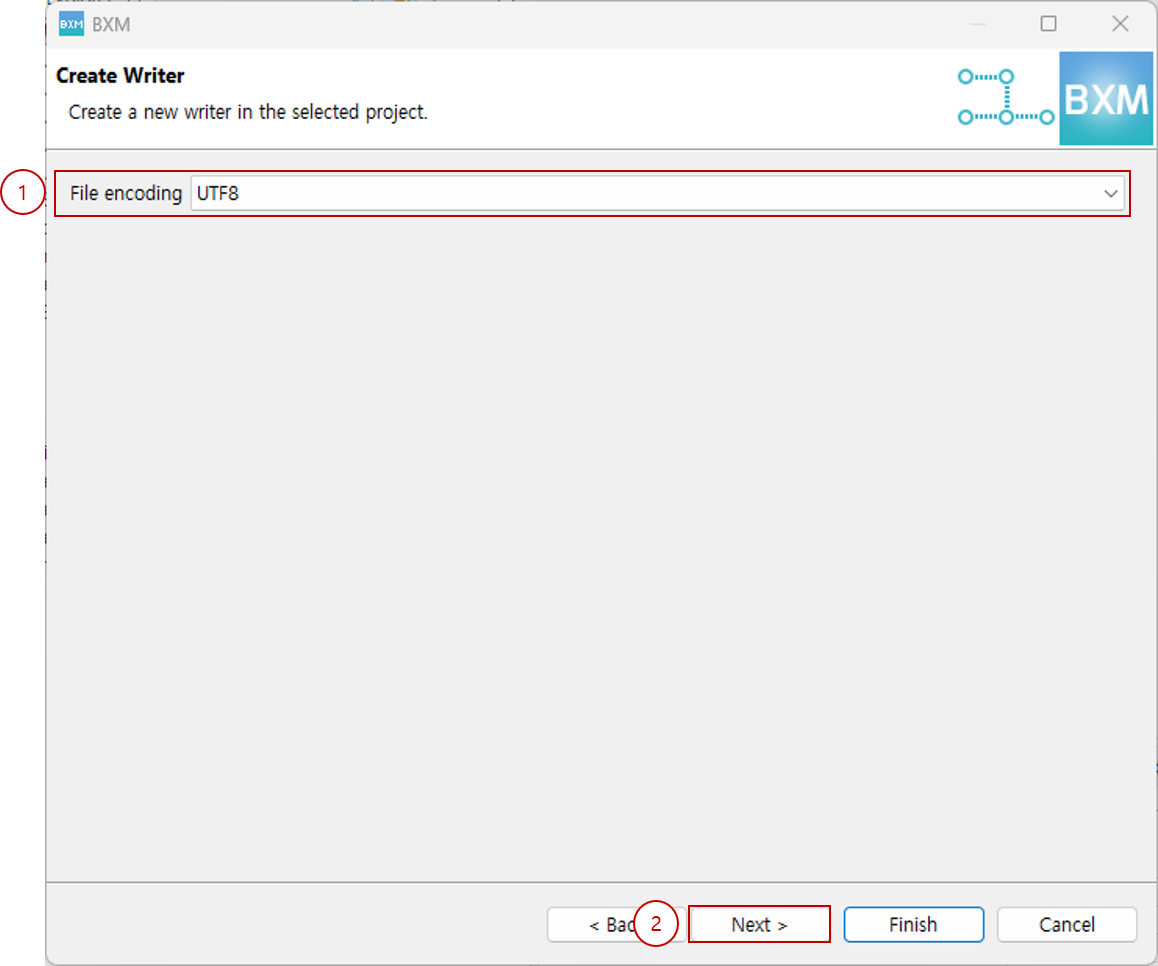
(1) Select file encoding
(2) Click Next
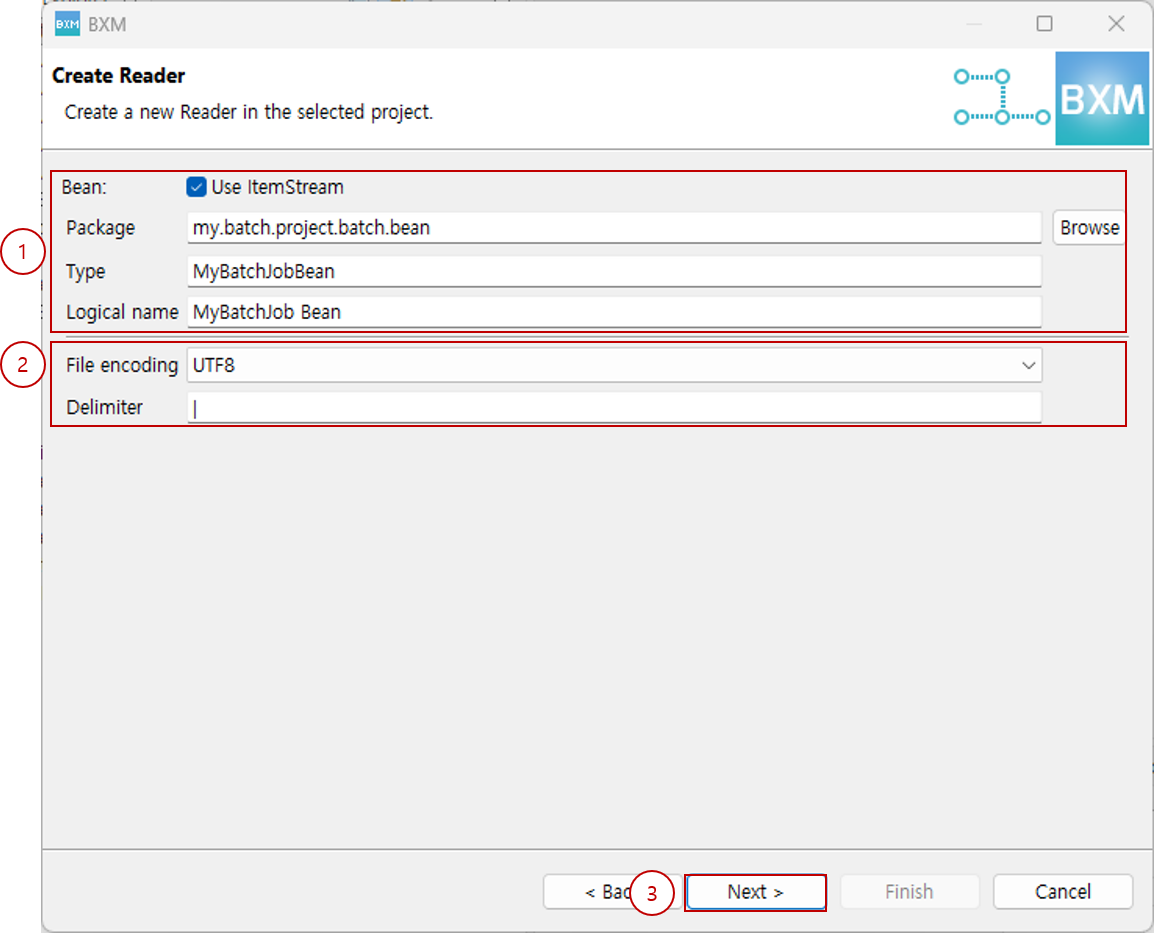
2.1.3. Delimited, MultiType Delimited Types
-
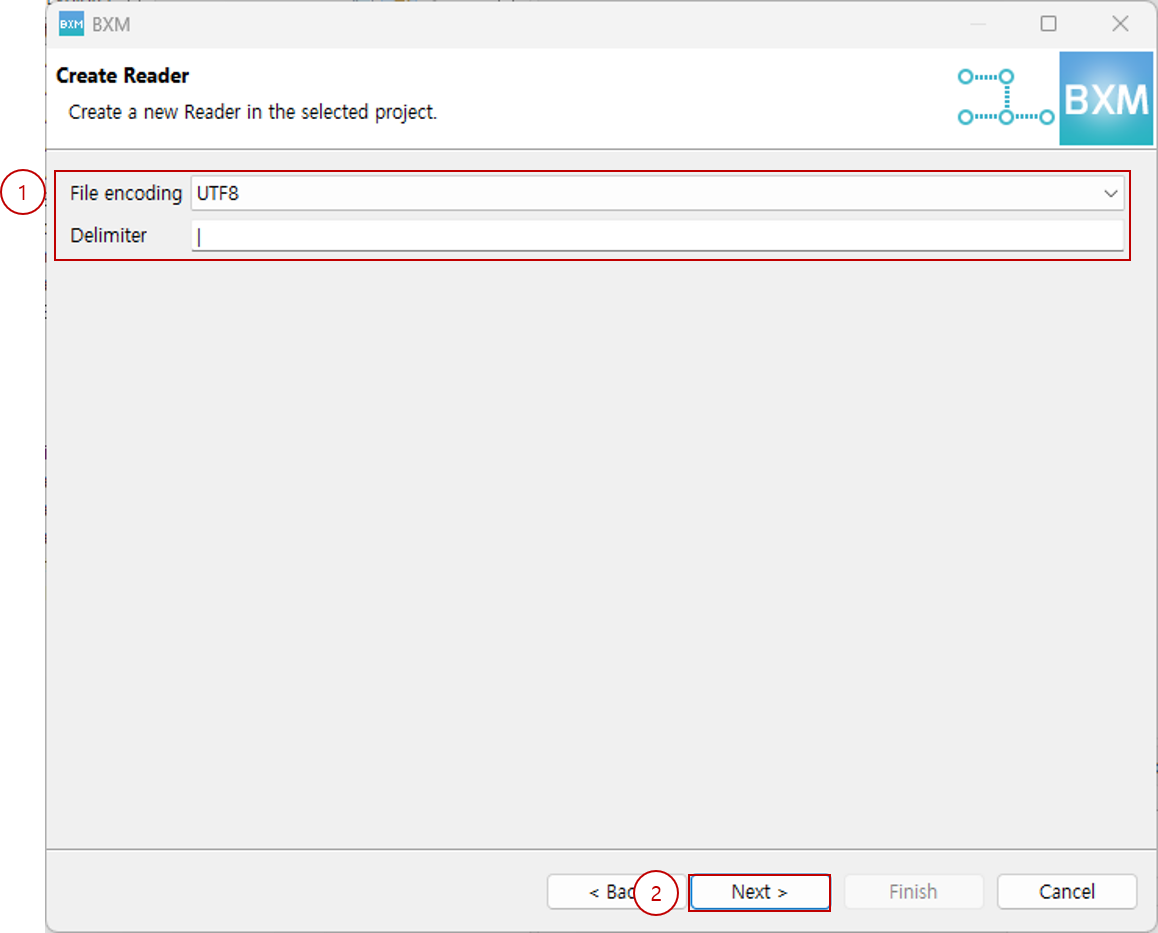
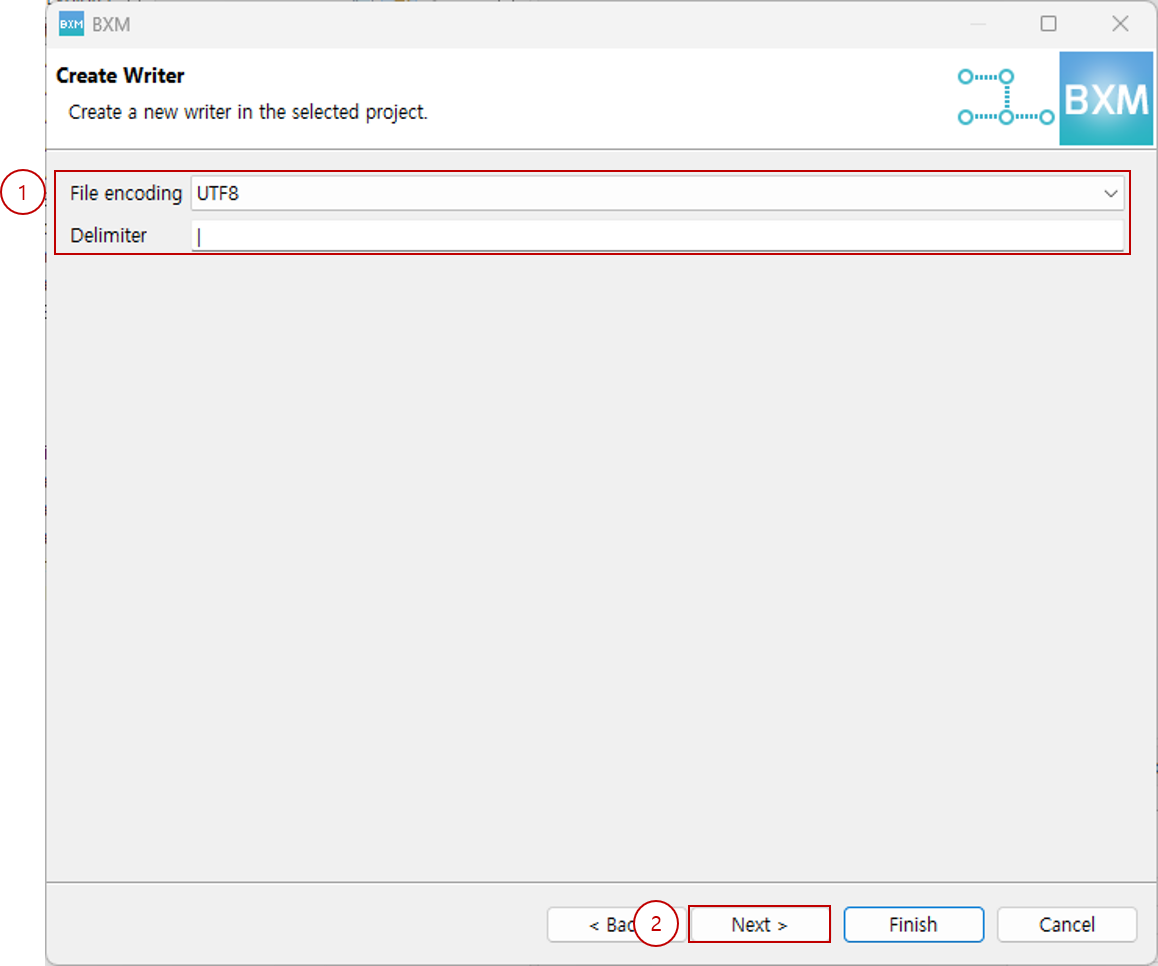
Select file encoding, enter delimiter, and click Next.
(1) Select file encoding and enter delimiter
(2) Click Next
2.1.4. File Read Source(Fixed) Type
-
Enter the Bean package, type, logical name, select file encoding, and click Next.
At this time, all resource names are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Enter the bean package, type, and logical name
(2) Select encoding
(3) Click Next
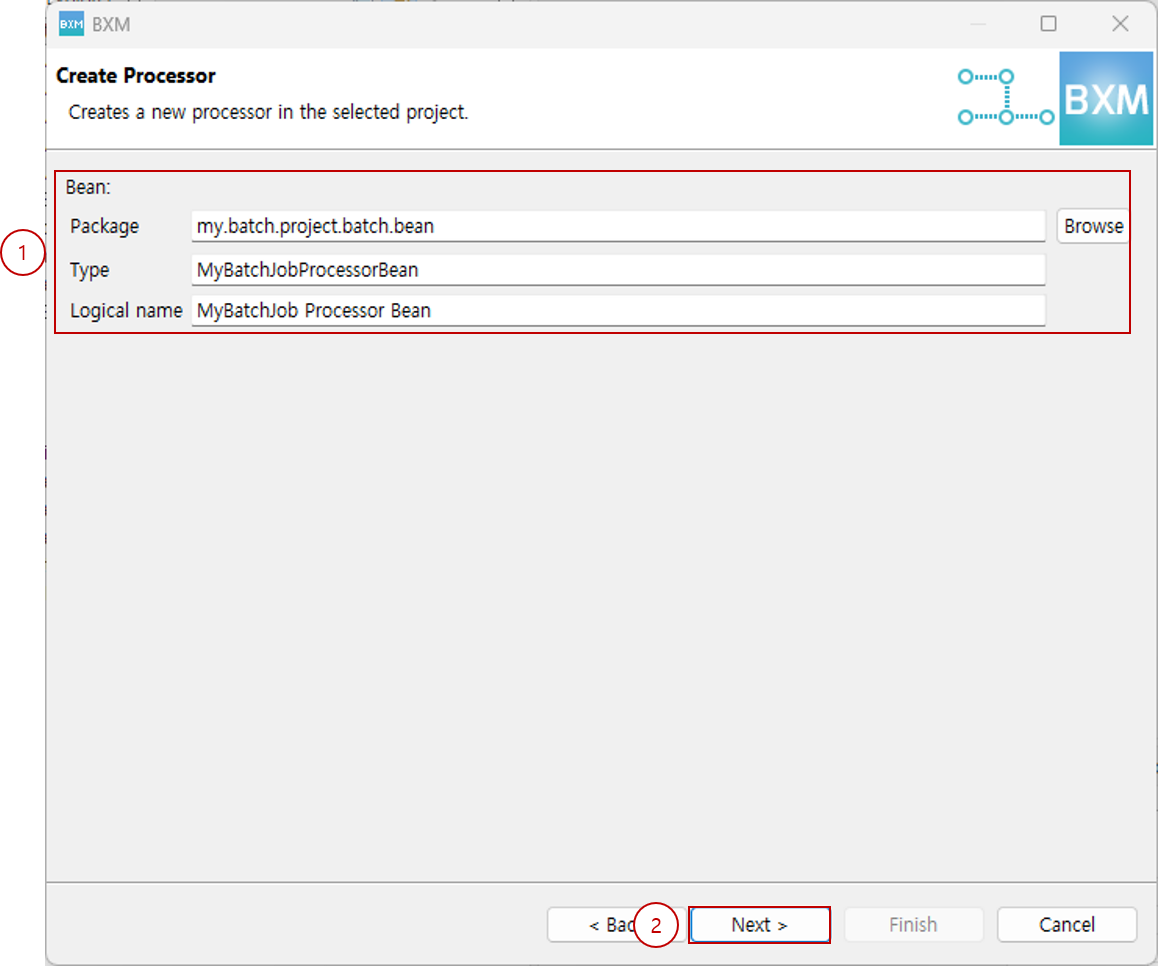
2.2. Processor Definition
Enter the required information for the Processor Bean.
-
Enter the Bean package, type, and logical name, then click Next.
At this time, all resource names are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator. Also, if Use reader class name is checked on the type selection page, this page is skipped.
(1) Enter the Bean package, type, and logical name
(2) Click Next
2.3. Definition by Writer Type
Enter the required information for each Writer type.
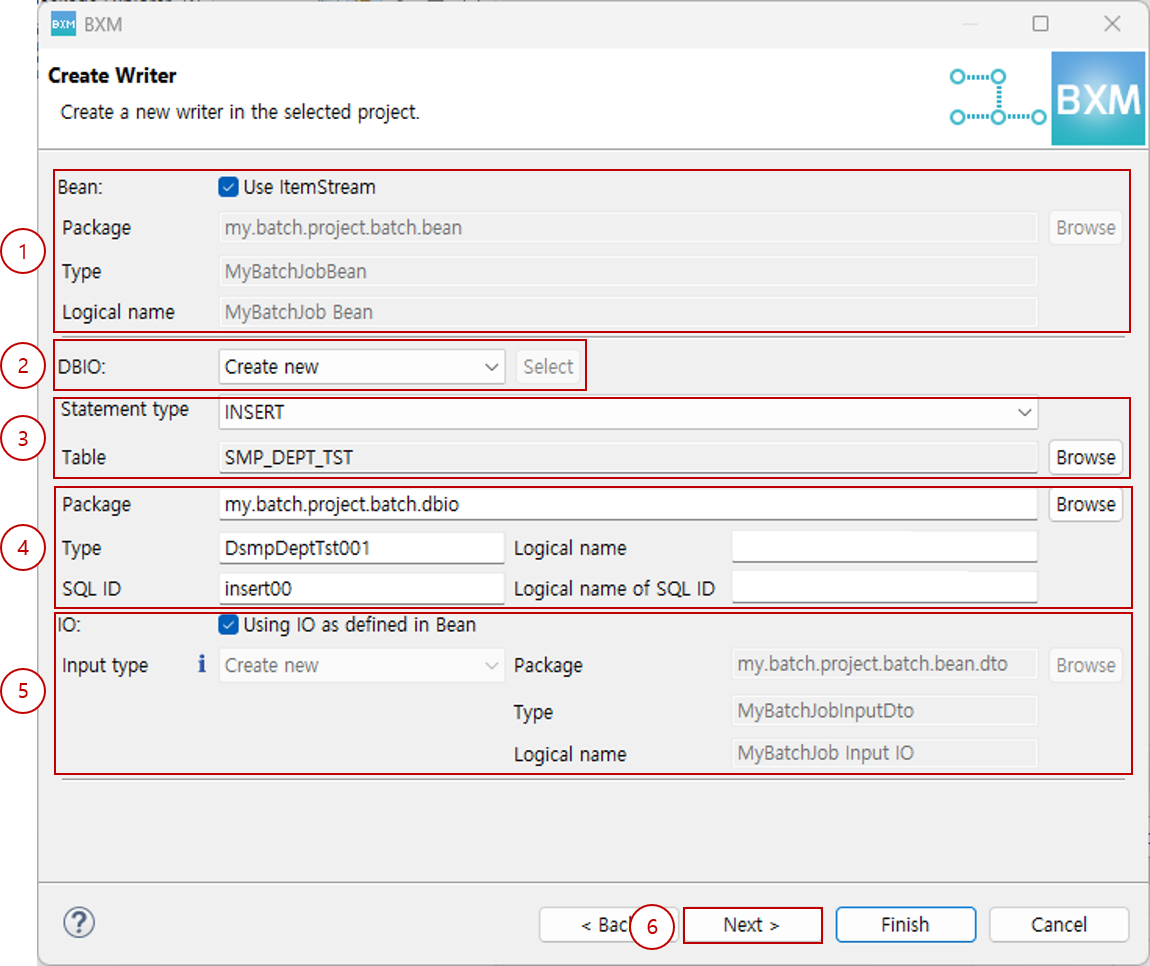
2.3.1. Database Type
-
Select the Bean package, type, logical name, statement type, and the desired table, then click Next.
At this time, all resource names are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Enter the Bean package, type, and logical name
(2) Select DBIO generation method (Create new, Select existing DBIO)
(3) Select statement type and table
(4) Enter DBIO package, type, logical name, SQL ID, and logical name of SQL ID
(5) Enter output type package, type, and logical name
(6) Click Next
2.3.2. Fixed, MultiType Fixed, Variable Types
-
Select file encoding and click Next.
(1) Select file encoding
(2) Click Next
2.3.3. Delimited, MultiType Delimited Types
-
Select file encoding, enter delimiter, and click Next.
(1) Select file encoding and enter delimiter
(2) Click Next
2.3.4. File Write Source(Fixed) Type
-
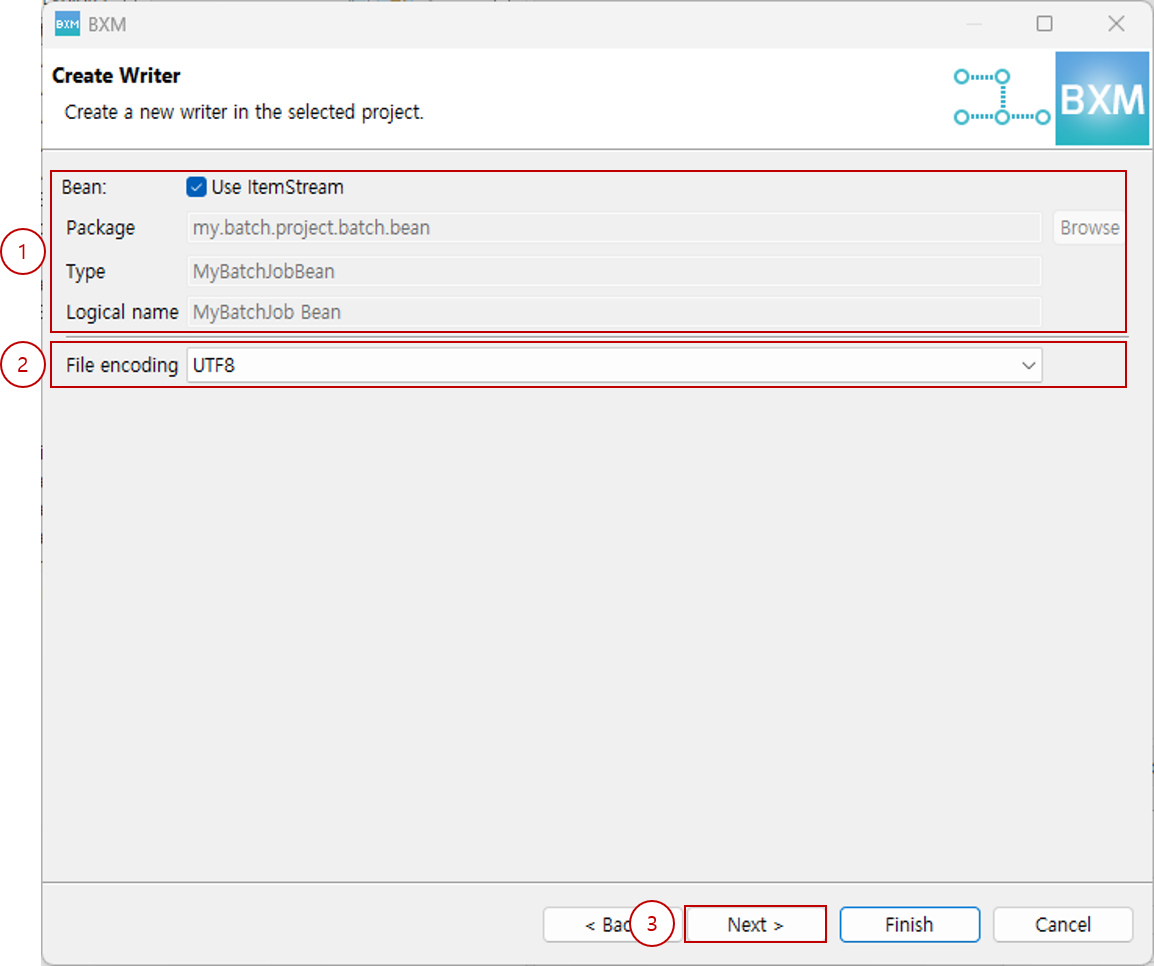
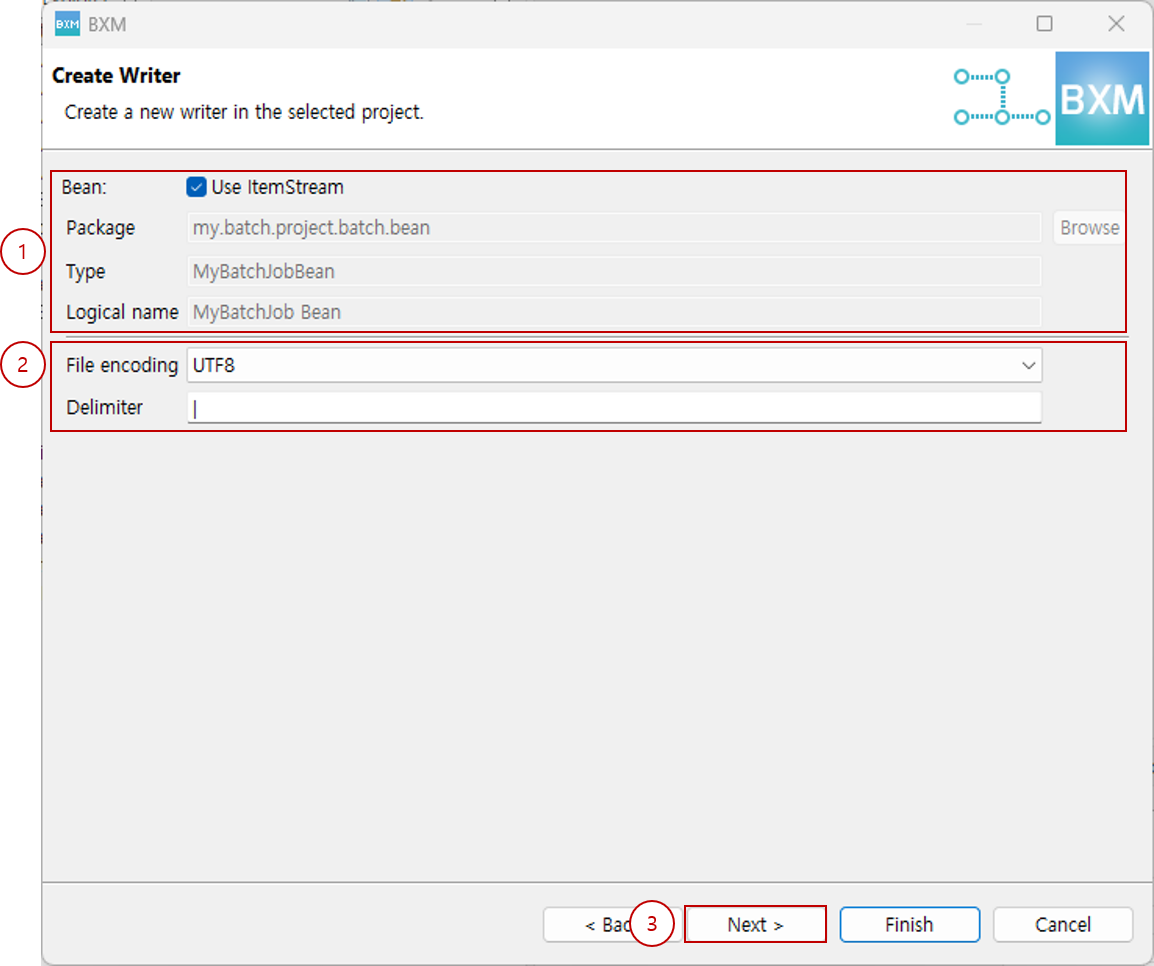
Enter the Bean package, type, logical name, select file encoding, and click Next.
At this time, all resource names are auto-completed by a module defined by the framework administrator.
(1) Enter the Bean package, type, and logical name
(2) Select encoding
(3) Click Next